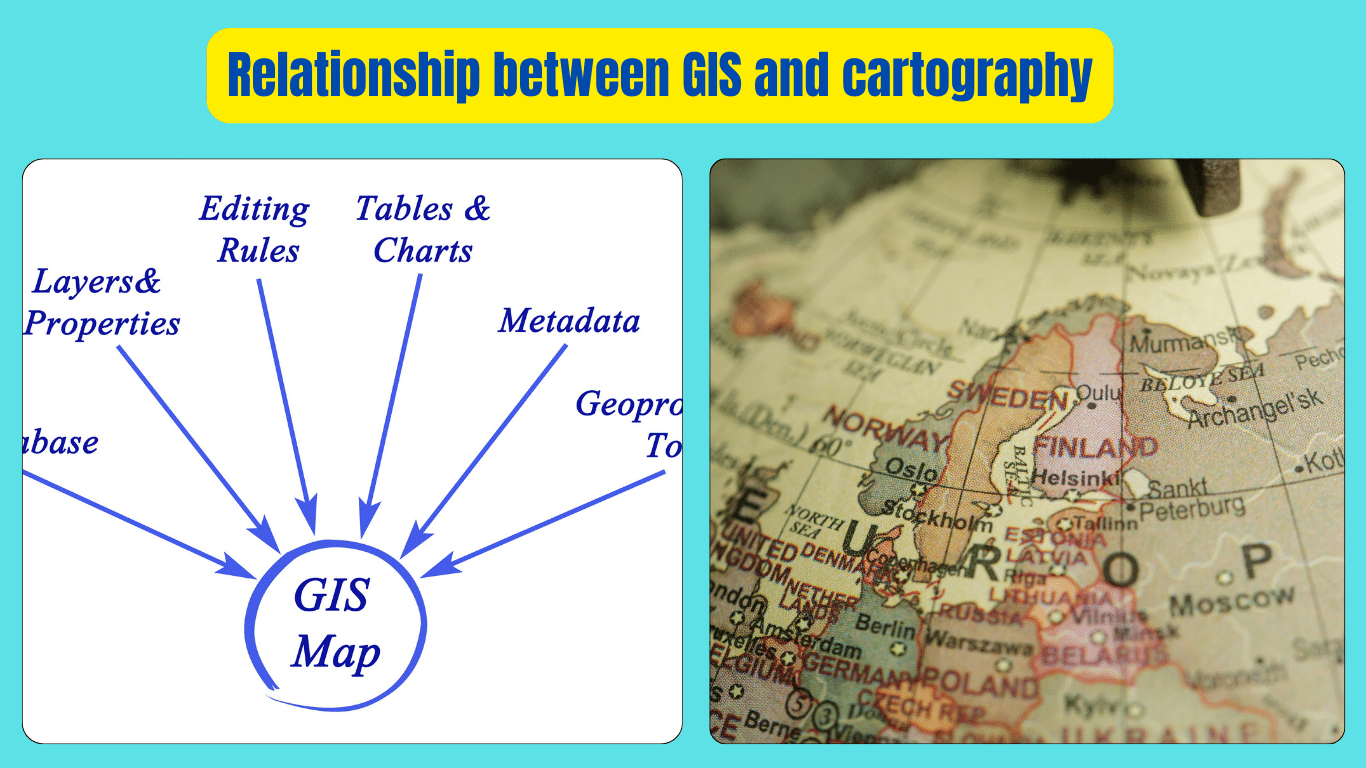
The relationship between GIS and cartography is fundamental to understanding and visualizing geographical data. Cartography, the art and science of mapmaking, has evolved alongside GIS technology, which allows us to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and present spatial data. GIS integrates various layers of geographic information, such as land use, population density, and natural resources, into interactive maps.
These maps created through GIS not only display geographical features but also enable users to explore and analyze data, making informed decisions about everything from urban planning to environmental management. Cartography provides the principles and techniques for designing visually appealing and informative maps, while GIS provides the tools to create dynamic, data-driven maps that can be continuously updated and customized. Together, GIS and cartography form a powerful partnership that enhances our understanding of the world around us and facilitates effective decision-making in various fields.
Understanding the Relationship between GIS and Cartography
In the realm of geography and spatial analysis, two key players stand out: GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and cartography. These two fields are closely intertwined, working hand in hand to help us understand and navigate the world around us. In this article, we’ll delve into the relationship between GIS and cartography, exploring how they complement each other and shape our understanding of geography.
What is GIS?
GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, is a powerful technology that allows us to capture, store, analyze, and present spatial data. At its core, GIS is all about understanding the relationship between different geographic features and phenomena. It enables us to visualize complex data sets in the form of maps, making it easier to interpret and analyze.
The Role of Cartography
Cartography, the art and science of mapmaking, plays a crucial role in GIS. While GIS provides the technological framework for working with spatial data, cartography provides the principles and techniques for designing effective maps. Cartographers use their expertise to create visually appealing and informative maps that communicate complex information clearly and concisely.
Integration of GIS and Cartography
The relationship between GIS and cartography is one of synergy. GIS provides the tools and capabilities for analyzing and manipulating spatial data, while cartography provides the design expertise to create meaningful visualizations. Together, they form a powerful combination that enables us to make sense of the world around us.
Creating Dynamic Maps
One of the key benefits of combining GIS and cartography is the ability to create dynamic maps. Unlike traditional paper maps, which are static and unchanging, GIS-powered maps can be updated in real time with the latest data. This allows users to explore and analyze spatial trends and patterns as they emerge, making informed decisions based on the most up-to-date information available.
Enhancing decision-making
GIS and cartography also play a crucial role in decision-making across various industries and sectors. From urban planning to environmental management, the ability to visualize spatial data enables policymakers and stakeholders to make more informed decisions. By overlaying different layers of geographic information, such as population density, land use, and natural resources, decision-makers can gain valuable insights into complex issues and identify potential solutions.
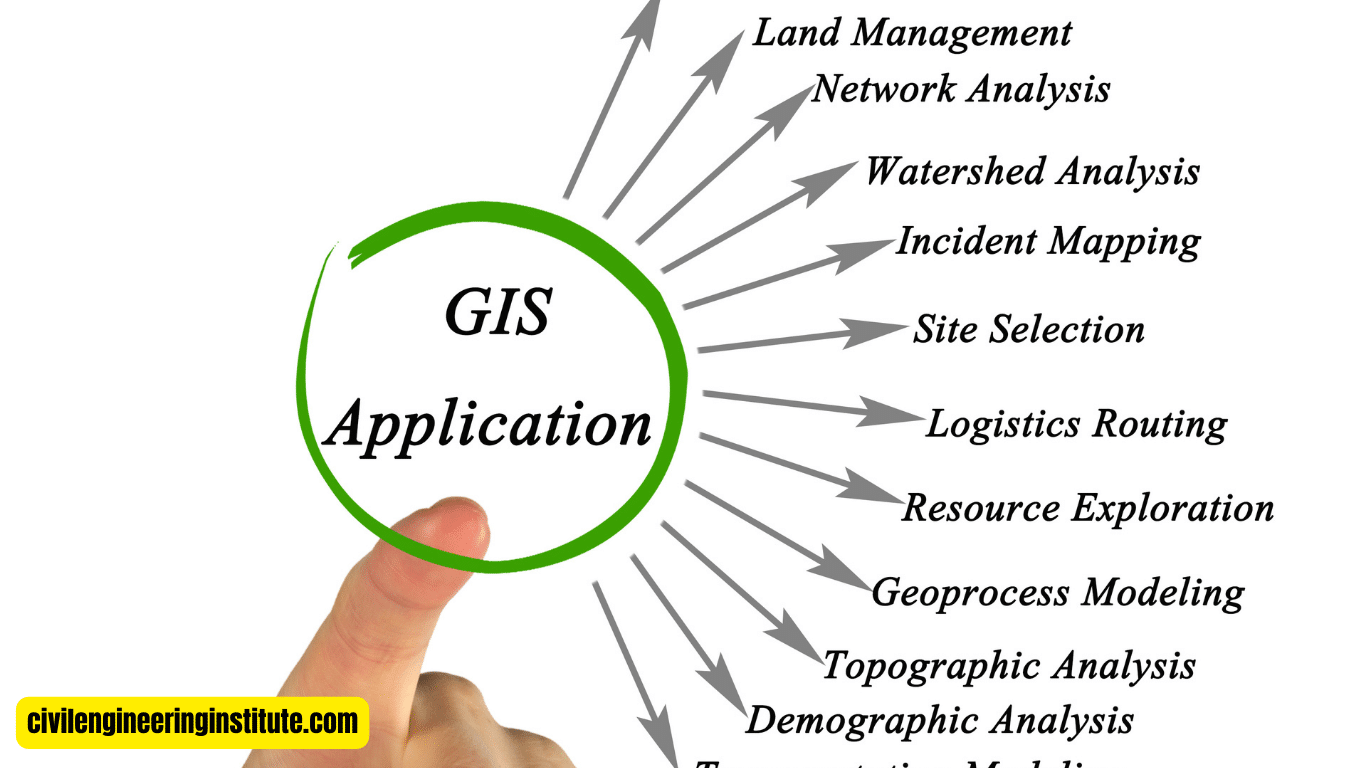
Applications of GIS and Cartography
The applications of GIS and cartography are diverse and far-reaching. In urban planning, GIS is used to analyze demographic trends, assess infrastructure needs, and plan for sustainable growth. In environmental science, GIS helps researchers study ecosystems, track wildlife populations, and monitor changes in the natural landscape. In emergency management, GIS is used to coordinate disaster response efforts, assess risk areas, and plan evacuation routes.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their many benefits, GIS and cartography also face challenges. One of the biggest challenges is the sheer volume of data that is now available. With the advent of technologies such as remote sensing and GPS, the amount of spatial data being generated is growing exponentially. This presents both opportunities and challenges for GIS and cartography professionals, who must find ways to manage and analyze increasingly large and complex data sets.
Some important key points: Relationship between GIS and cartography
Relationship between GIS and cartography
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) plays a vital role in modern cartography by providing advanced tools and techniques for mapmaking. One of the key uses of GIS in cartography is its ability to integrate various layers of geographic data, such as terrain, land use, and population density, into comprehensive maps. GIS enables cartographers to overlay and analyze different data sets, allowing them to create maps that are not only visually appealing but also rich in information.
Additionally, GIS facilitates the creation of dynamic maps that can be updated in real time, ensuring that maps always reflect the most current data available. Moreover, GIS enables cartographers to perform spatial analysis, such as identifying patterns and trends within geographic data, which further enhances the usefulness and effectiveness of maps.
Relationship between GIS and Geography
GIS and geography share a close relationship, as GIS is a powerful tool used within the field of geography to analyze and visualize spatial data. Geography is the study of the Earth’s surface and the processes that shape it, while GIS provides the technological framework for working with geographic information.
GIS enables geographers to capture, store, analyze, and present geographic data in meaningful ways, helping them to better understand the world around us. The relationship between GIS and geography is symbiotic, with GIS providing the tools and capabilities needed to conduct spatial analysis, while geography provides the context and framework for interpreting the results.
Differences between Cartography, Remote Sensing, and GIS
While cartography, remote sensing, and GIS are all related fields within geography, they serve different purposes and employ different techniques. Cartography is the art and science of mapmaking, focusing on the design and creation of maps. Remote sensing involves the use of satellite or aerial imagery to collect data about the Earth’s surface from a distance.
GIS, on the other hand, is a technology that allows for the capture, storage, analysis, and presentation of geographic data. While cartography and remote sensing are both important components of GIS, they each have their own distinct methodologies and applications.
Differences between GIS and Computer-Assisted Cartography
GIS and computer-assisted cartography are closely related but have some key differences. GIS is a comprehensive system that encompasses not only mapmaking but also the analysis and manipulation of geographic data. It allows users to perform spatial analysis and create dynamic, interactive maps. Computer-assisted cartography, on the other hand, refers specifically to the use of computers to aid in the design and production of maps. While GIS includes computer-assisted cartography as one of its components, it also offers additional capabilities such as data management and spatial analysis.
Similarities between GIS and Cartography
Despite their differences, GIS and cartography share several similarities. Both disciplines are concerned with the visualization and analysis of geographic data. They both aim to represent spatial information clearly and understandably, whether it be through traditional paper maps or interactive digital maps.
Additionally, both GIS and cartography rely on principles of design and aesthetics to create visually appealing maps that effectively communicate information to users. While GIS may offer more advanced tools and capabilities, the fundamental goal of both GIS and cartography remains the same: to create informative and useful maps.
Differences between GIS and Computer Cartography
GIS and computer cartography are often used interchangeably, but they are not synonymous. GIS is a broader field that encompasses not only the design and production of maps but also the analysis and manipulation of geographic data. GIS software allows users to perform spatial analysis, such as identifying patterns and trends within geographic data sets. Computer cartography, on the other hand, refers specifically to the use of computers to aid in the design and production of maps. While GIS includes computer cartography as one of its components, it also offers additional capabilities beyond traditional computer cartography, such as data management and spatial analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between GIS and cartography is one of collaboration and mutual benefit. GIS provides the technological infrastructure for working with spatial data, while cartography provides the design expertise to create meaningful visualizations. Together, they form a powerful combination that enables us to explore, analyze, and understand the world around us in new and innovative ways. As technology continues to evolve and new data sources become available, the relationship between GIS and cartography will only grow stronger, shaping the future of geography and spatial analysis.
FAQs
What is GIS, and how does it relate to cartography?
GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, is a technology that helps us work with geographic data. It’s closely related to cartography because it helps us make maps and understand spatial information.
How does cartography use GIS technology?
Cartography uses GIS tools to create maps that are more accurate and informative. GIS helps cartographers gather, analyze, and present geographical data effectively.
Can you explain how GIS and cartography work together?
GIS provides the digital framework for cartographers to organize and visualize geographic data. Cartography then uses this data to design maps that are easy to read and understand.
What are the benefits of combining GIS and cartography?
Combining GIS and cartography allows us to create dynamic maps with layers of information. These maps are not only visually appealing but also interactive and rich in detail.
How do GIS and cartography help in urban planning?
GIS and cartography are essential in urban planning because they help identify areas for development, analyze transportation networks, and understand population distribution.
Can GIS and cartography be used in environmental studies?
Yes, GIS and cartography are valuable tools in environmental studies. They help researchers map ecosystems, track wildlife habitats, and monitor changes in the environment over time.
What skills are needed to work in GIS and cartography?
To work in GIS and cartography, you need a combination of technical skills, such as using GIS software, and artistic skills, like understanding design principles for creating maps.
Are GIS and cartography used in disaster management?
Absolutely. GIS and cartography help emergency responders by mapping out disaster-prone areas, planning evacuation routes, and coordinating relief efforts during and after disasters.
Can I use GIS and cartography in everyday life?
Yes! GIS and cartography are everywhere, from using GPS navigation apps to find directions to viewing weather maps on your phone. They help us understand our surroundings better.
How are GIS and cartography evolving with technology?
With advances in technology, GIS and cartography are becoming more accessible and powerful. We now have tools like interactive online maps and 3D visualization techniques that make understanding spatial data easier than ever.