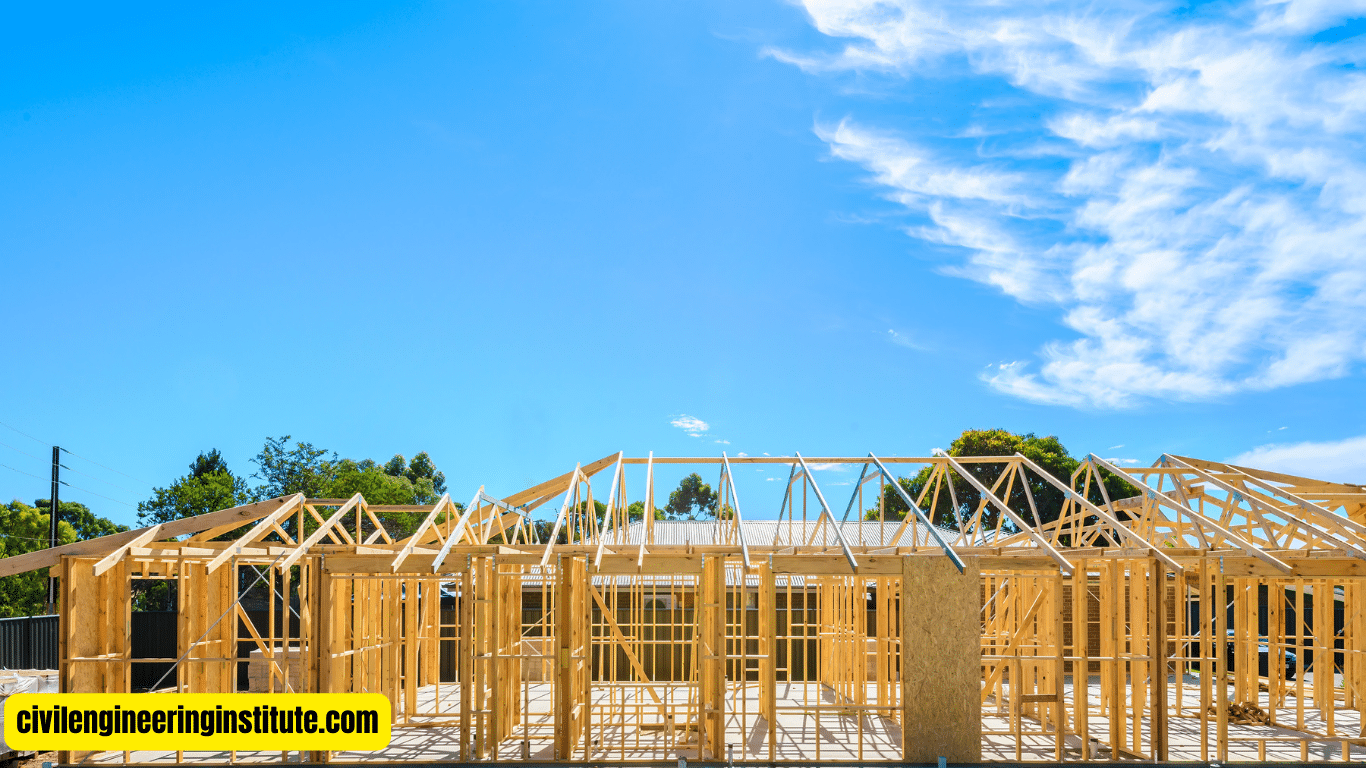
How Timber frame houses are built by using a construction method that utilizes wooden frames as the primary structural support. The process begins with the preparation of the timber, which is often sourced from sustainably managed forests. The timber is then cut and assembled into frames, typically consisting of vertical posts (known as studs), horizontal beams (known as plates), and diagonal braces for added stability. These frames are erected on the foundation of the house and secured into place.
Once the frame is in place, other elements such as floors, walls, and roofs are added using a variety of techniques, including sheathing and insulation. Timber frame houses offer numerous benefits, including energy efficiency, durability, and environmental sustainability. Additionally, the open design of timber frame construction allows for flexible floor plans and architectural creativity. Overall, the process of building a timber frame house combines traditional craftsmanship with modern construction techniques to create homes that are both beautiful and functional.
Exploring the Construction Process of Timber Frame Houses: From Trees to Homes
Timber frame houses have been a popular choice for homeowners for centuries, thanks to their timeless appeal and sturdy construction. But have you ever wondered how these charming homes are built? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take a closer look at the process of constructing timber frame houses, breaking down each step from sourcing the materials to the finished product.
Understanding Timber Frame Construction
Before delving into the construction process, let’s first understand what timber frame construction entails. Timber frame houses are built using wooden frames as the primary structural support. These frames are typically made from solid wood, such as pine, cedar, or oak, and are assembled using traditional joinery techniques.
Sourcing and Preparation of Timber
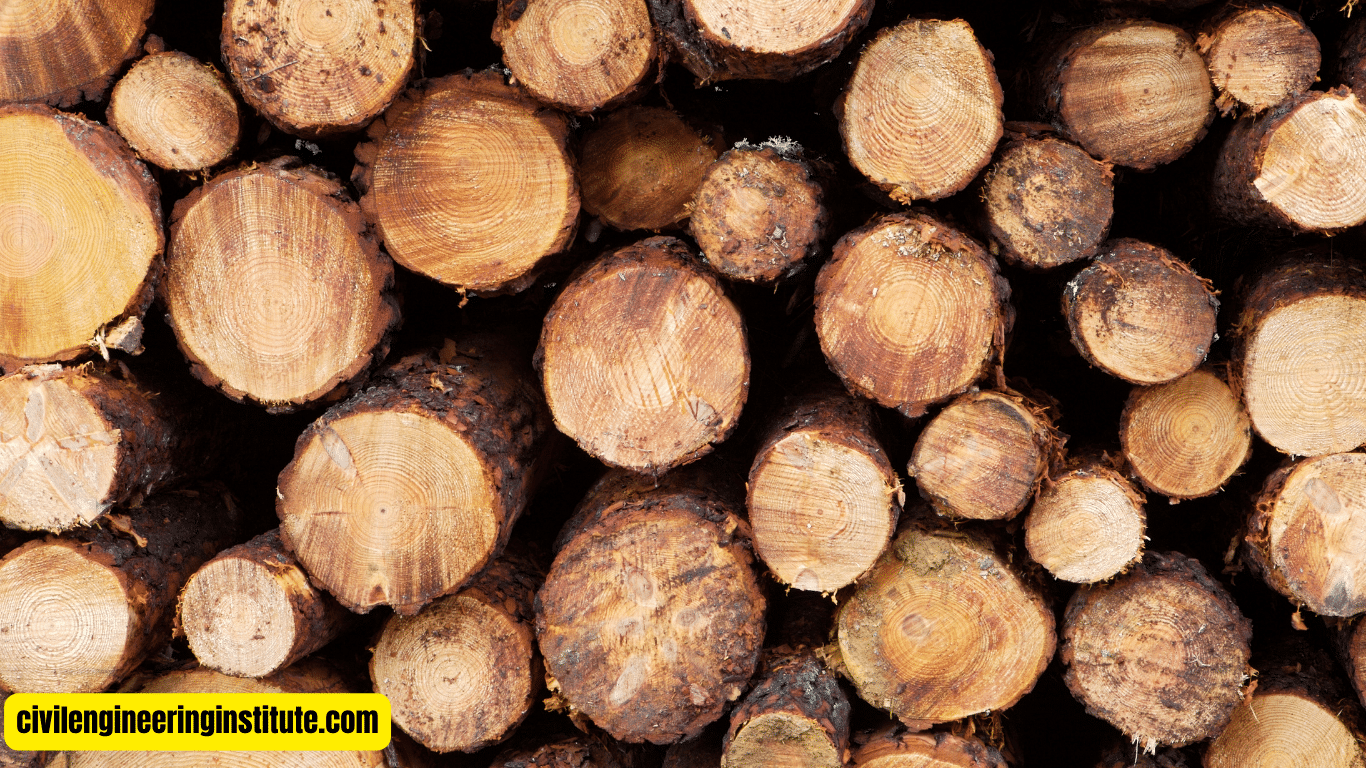
The construction process begins with sourcing the timber, which is often sourced from sustainably managed forests. Trees are carefully selected and harvested, then transported to a sawmill, where they are cut into lumber of various dimensions. The lumber is then kiln-dried to remove excess moisture, ensuring stability and durability.
Frame Assembly
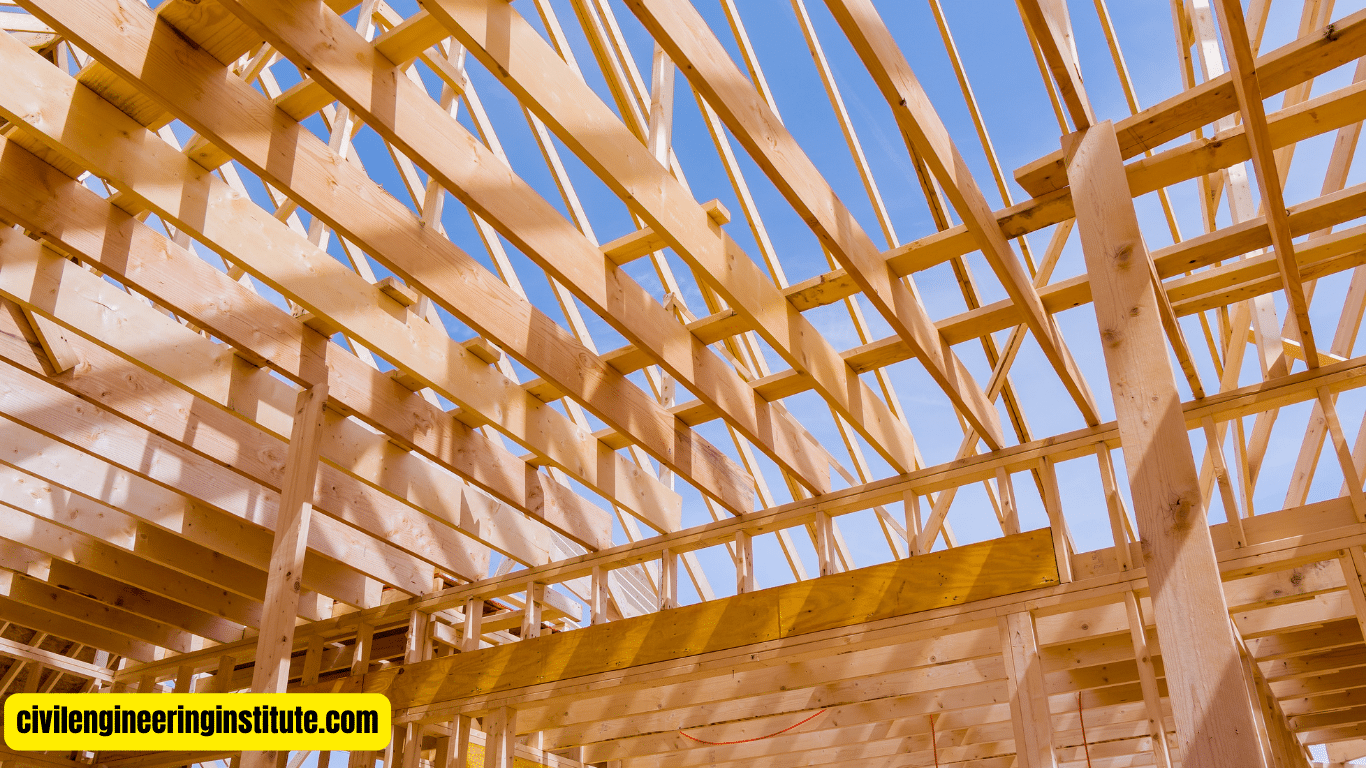
Once the timber has been prepared, it’s time to assemble the frame of the house. This involves cutting the timber into the required lengths and shapes, then joining them together using traditional joinery techniques such as mortise and tenon or dovetail joints. The frame typically consists of vertical posts (studs), horizontal beams (plates), and diagonal braces for added stability.
Erection of the Frame
With the frame components prepared, the next step is to erect the frame on the foundation of the house. The frame is carefully positioned and secured into place, forming the skeleton of the house. This is a critical step in the construction process, as it establishes the structural integrity of the building.
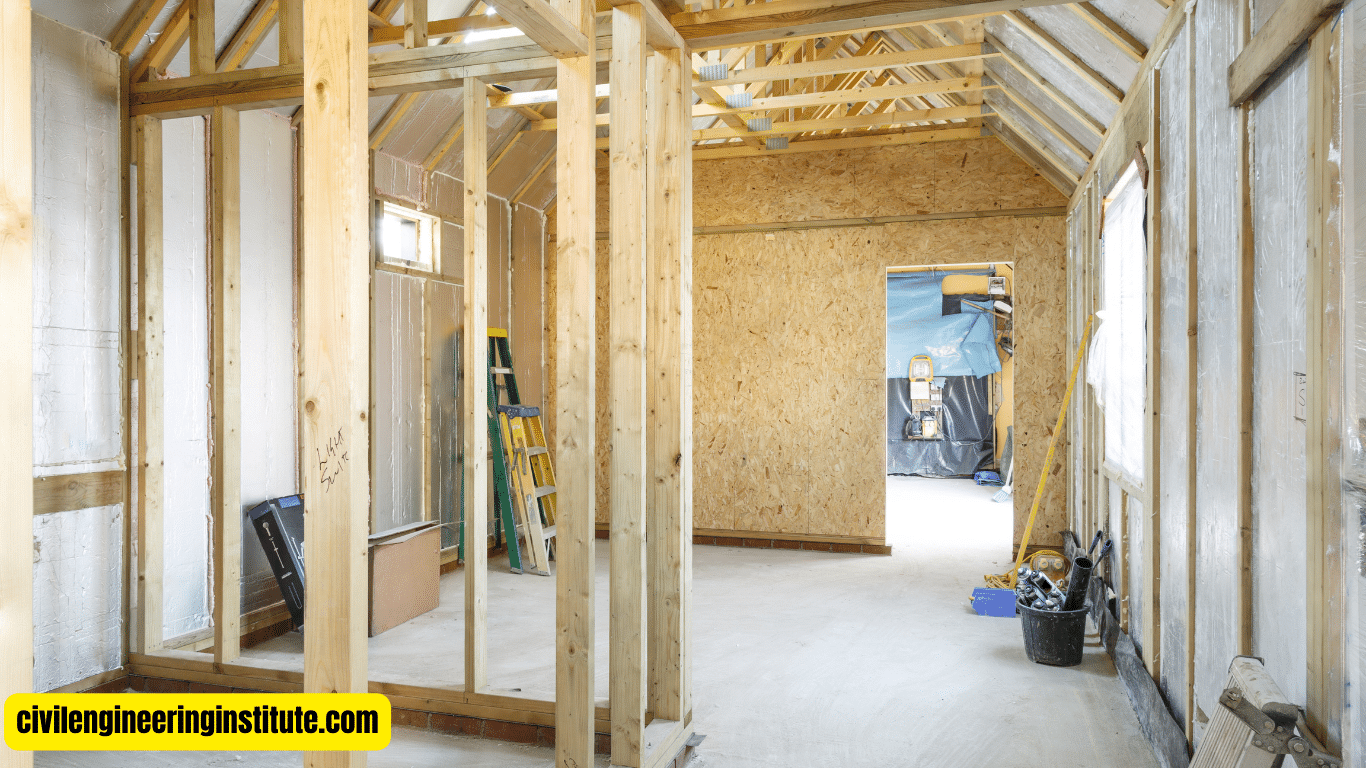
Addition of Secondary Elements
Once the frame is in place, secondary elements such as floors, walls, and roofs are added to complete the structure. Flooring materials, such as plywood or oriented strand board (OSB), are installed on the floor joists, while exterior walls are typically sheathed with plywood or oriented strand board and insulated to improve energy efficiency.
Roof Construction
Roof construction in timber-framed houses can vary depending on the design preferences of the homeowner. Common roof types include gable roofs, hip roofs, and shed roofs. Roof trusses or rafters are used to support the roof structure, and roofing materials such as shingles or metal panels are installed to protect it from the elements.
Interior Finishing
Once the basic structure of the house is complete, interior finishing work begins. This may include installing drywall, trim, doors, and windows, as well as painting or staining the interior surfaces. Flooring materials such as hardwood, tile, or carpeting are also installed to complete the interior space.
Exterior Finishing
Finally, exterior finishing touches are added to enhance the curb appeal of the timber frame house. This may include siding materials such as wood, vinyl, or fiber cement, as well as exterior trim and decorative elements. Landscaping and outdoor amenities such as decks or porches may also be added to further enhance the exterior appearance of the home.
Some Key Points: How timber frame houses are built
Disadvantages of Timber-Framed Construction
While timber frame construction offers numerous advantages, it also has some disadvantages to consider. One drawback is the potential for moisture-related issues, such as rot and mold, if the timber is not properly treated or maintained. Additionally, timber frame houses may require more frequent maintenance compared to other construction methods. Fire resistance can also be a concern, as timber is combustible, although fire-resistant treatments and building codes help mitigate this risk.
The foundation of a Timber Frame House
The foundation of a timber frame house plays a crucial role in providing structural support and stability to the entire structure. Typically, timber frame houses are built on a foundation made of concrete, which is poured into trenches or forms to create a solid base. The foundation helps distribute the weight of the house evenly and prevents settling or shifting over time.
Difficulty of Building a Timber Frame House
Building a timber frame house requires specialized knowledge and skills, but it is not necessarily harder than other construction methods. With proper planning, preparation, and guidance from experienced professionals or resources, individuals with basic carpentry skills can successfully build a timber frame house. However, attention to detail and adherence to building codes are essential to ensuring a safe and structurally sound final product.
Issues with Timber Frame
One common issue with timber frame construction is the potential for thermal bridging, where heat escapes through the solid wood members of the frame. This can result in reduced energy efficiency and higher heating and cooling costs. Additionally, if the timber is not properly dried or seasoned, it may shrink or warp over time, leading to structural problems or cosmetic issues.
Supporting Walls in Timber-Framed Houses
In timber-framed houses, the timber frame itself provides structural support, eliminating the need for load-bearing interior walls. This allows for greater flexibility in interior design and floor plan layout, as walls can be placed wherever desired without affecting the structural integrity of the house.
Materials Used for Walls in Timber Frame Houses
The walls in a timber frame house are typically made of a combination of materials, including solid wood studs, sheathing panels such as plywood or oriented strand board (OSB), and insulation. These materials work together to provide structural support, thermal insulation, and moisture protection for the house.
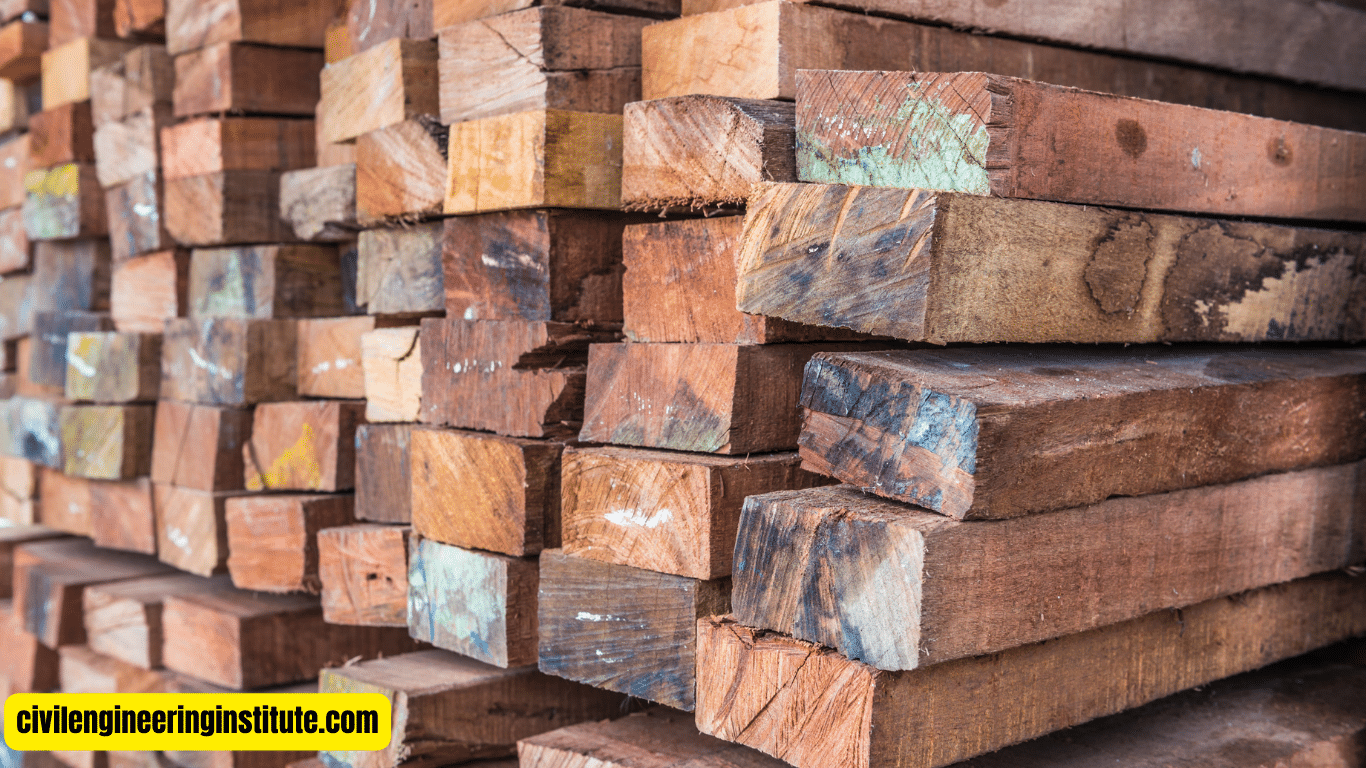
Best Timber for House Frame
The best timber for a house frame depends on factors such as availability, cost, and desired characteristics. Commonly used timber species for house framing include Douglas fir, spruce, pine, and cedar. These species are known for their strength, durability, and suitability for structural applications.
Life Expectancy of a Timber Frame House
With proper maintenance and care, a timber-framed house can have a life expectancy comparable to that of houses built using other construction methods. The longevity of a timber frame house depends on factors such as the quality of materials and construction, exposure to environmental conditions, and regular maintenance practices.
Cost Considerations for Timber Frame Construction
Timber frame construction can be more expensive upfront compared to other construction methods, primarily due to the cost of materials and the specialized labor required. However, timber-framed houses may offer long-term cost savings in terms of energy efficiency, durability, and maintenance. It’s essential to weigh the upfront costs against the long-term benefits when considering timber frame construction.
Thickness of Timber Frame Walls
The thickness of timber frame walls can vary depending on factors such as insulation requirements and structural considerations. Typically, timber frame walls range from 4 to 8 inches in thickness, with additional space allocated for insulation. The thickness of the walls may also vary depending on local building codes and climate conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the construction process of timber frame houses is a meticulous and time-honored craft that combines traditional woodworking techniques with modern construction methods. From sourcing the timber to the final finishing touches, each step in the process requires careful attention to detail and craftsmanship. The result is a beautiful and durable home that embodies the timeless charm of timber frame construction. Whether you’re considering building a timber frame house or simply curious about the construction process, understanding how these homes are built can deepen your appreciation for this centuries-old building tradition.
FAQs
What is a timber-framed house?
A timber-frame house is a type of home construction that utilizes wooden frames as the primary structural support.
How are timber frame houses built?
Timber frame houses are built by assembling wooden frames made of vertical posts (studs), horizontal beams (plates), and diagonal braces. These frames are then erected on a foundation and filled in with walls, floors, and roofs.
What materials are used to build timber-framed houses?
Timber frame houses are typically constructed using solid wood for the frames, along with sheathing panels such as plywood or oriented strand board (OSB), insulation, and exterior siding materials.
Are timber frame houses environmentally friendly?
Yes, timber-framed houses are considered environmentally friendly because wood is a renewable resource that can be sustainably harvested. Additionally, timber frame construction requires less energy to produce compared to other building materials.
Do timber-frame houses require special maintenance?
Timber frame houses may require regular maintenance to ensure their longevity and structural integrity. This may include periodic inspections for rot or insect damage and applying protective finishes to the wood.
Are timber frame houses energy-efficient?
Timber-framed houses can be energy-efficient when properly insulated and sealed. The solid wood frames provide excellent thermal insulation, and additional insulation can be added between the frames to further enhance energy efficiency.
How long does it take to build a timber frame house?
The time it takes to build a timber frame house can vary depending on factors such as the size and complexity of the design, site conditions, and the availability of labor and materials. On average, the construction of a timber-framed house can take several months to a year.
Can I customize the design of a timber frame house?
Yes, timber frame houses offer flexibility in design, allowing homeowners to customize the layout, floor plan, and architectural features according to their preferences and needs.
Are timber-framed houses structurally strong?
Yes, timber-framed houses are known for their structural strength and durability. The solid wood frames provide excellent support, and when properly constructed, timber frame houses can withstand various environmental conditions.
Are timber-framed houses suitable for all climates?
Timber frame houses can be designed to be suitable for different climates, with appropriate insulation and construction techniques to address specific climate challenges such as extreme temperatures, humidity, or precipitation.