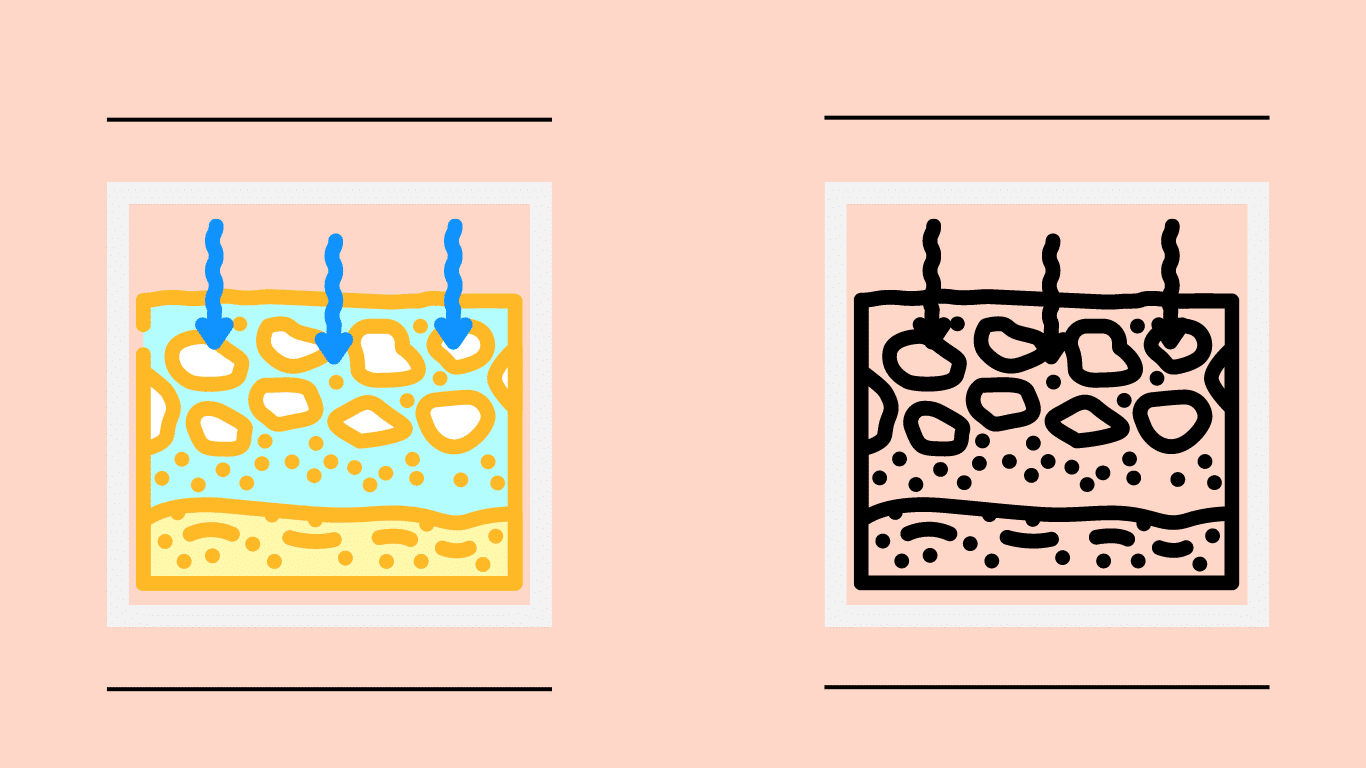
why is permeability of soil important The permeability of soil is fundamental to the soil; it determines how water and other liquids move through it. Think of soil like a sponge: if it’s very permeable, water can easily pass through, which is good for plants because their roots can access the water they need. However, if the soil isn’t permeable enough, water might get stuck on the surface or even cause flooding.
This can drown plants and make it hard for them to grow. So, knowing how permeable soil is helps farmers and gardeners figure out the best way to manage water and grow healthy crops. Additionally, understanding soil permeability is important for engineers and builders when designing structures like roads and buildings, as it helps them plan for proper drainage and prevent issues like erosion and water damage.
Let’s understand why is permeability of soil important.
Soil is more than just dirt under our feet. It’s a complex ecosystem that plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth. One crucial characteristic of soil that often goes unnoticed is its permeability. But what exactly is soil permeability, and why is it so important? Let’s delve into this topic to understand its significance.
What is Soil permeability?
Soil permeability refers to the ability of soil to allow water or other fluids to pass through it. Think of it like a sponge – some soils soak up water quickly, while others may let water pass through slowly. Permeability depends on various factors, including soil composition, texture, structure, and the presence of pores or spaces between soil particles.
why is permeability of soil important?
- Water Management
- Plant Growth
- Nutrient Transport
- Environmental Impact
- Soil Health
Water Management:
One of the primary reasons soil permeability matters is its role in water management. When rain falls, permeable soil absorbs water like a sponge, preventing runoff and reducing the risk of flooding. This absorption also helps replenish underground water sources, such as aquifers, which are crucial for drinking water and irrigation.
Plant Growth:
Plants depend on soil for nutrients and water. If soil is too compacted or impermeable, water may pool on the surface or drain away too quickly, depriving plants of the moisture they need to thrive. Permeable soil allows water to penetrate deeper, reaching plant roots and promoting healthy growth.
Nutrient Transport:
Apart from water, soil also transports essential nutrients to plants. Permeability ensures that nutrients dissolved in water can penetrate the soil and reach plant roots effectively. Without proper permeability, nutrients may be washed away by surface runoff, leading to soil depletion and reduced fertility.
Soil Health:
Healthy soil is alive with microorganisms that play vital roles in decomposition, nutrient cycling, and overall ecosystem function. Adequate soil permeability provides oxygen to these organisms, maintaining a balanced ecosystem within the soil. In contrast, poorly permeable soil can become compacted and anaerobic, hindering microbial activity and compromising soil health.
Environmental Impact:
Soil permeability also affects the environment in various ways. Impermeable surfaces, such as concrete or compacted soil, contribute to urban heat islands and increase the risk of pollution runoff into waterways. By maintaining soil permeability, we can mitigate these environmental impacts and promote sustainable land use practices.
Here are some key points about soil permeability in simple language:
- Soil permeability is how easily water and other liquids move through the soil.
- It’s important for managing water, preventing flooding, and replenishing underground water sources.
- Permeable soil helps plants by allowing water and nutrients to reach their roots.
- Healthy soil needs permeability for oxygen flow to microorganisms that keep the ecosystem balanced.
- Impermeable surfaces like concrete can lead to environmental problems like pollution runoff.
- Understanding and maintaining soil permeability is crucial for sustainable land use and a healthy environment.
Usually, many people ask some of their questions daily so here are some of the queries I am trying to discuss
What is permeability and why is it important?
Permeability refers to how easily liquids or gases can pass through a substance, like soil. It’s crucial because it affects many aspects of the environment, agriculture, and everyday life. In soil, permeability determines how well water can move through it, which is vital for plant growth and farming.
What is the importance of permeability of soil?
The permeability of soil is essential because it directly influences how water moves through the ground. When soil is permeable, water can penetrate deep into the soil, reaching plant roots and providing them with the necessary moisture. Without proper permeability, water might pool on the surface or runoff, leading to soil erosion and poor plant growth.
Why is permeability important to plant growth?
For plants, permeability is vital for their roots to access water and nutrients. If soil is too compact or impermeable, roots struggle to penetrate and absorb what they need for healthy growth. Proper permeability ensures that plants can thrive by accessing essential resources underground.
What is permeability and why is it important to farmers?
Farmers rely on soil permeability to manage water effectively for their crops. Soil with high permeability allows for efficient irrigation and drainage, preventing waterlogging and ensuring that crops receive the right amount of moisture. This helps maximize crop yield and quality.
What happens if soil is not permeable?
If soil lacks permeability, it can lead to various problems. Water might accumulate on the surface, causing flooding and waterlogging, which can drown plants and promote diseases. Additionally, poor permeability can hinder root growth and nutrient uptake, affecting plant health and agricultural productivity.
Why is high permeability good?
High permeability is beneficial because it allows water to infiltrate quickly into the soil, reducing surface runoff and erosion. It also facilitates proper aeration of the soil, promoting microbial activity and nutrient cycling, which are essential for healthy soil and plant growth.
What is a good permeability soil?
A good permeability soil is one that strikes a balance between allowing water to infiltrate and retaining enough moisture for plants. Sandy soils generally have higher permeability due to their coarse texture, while clay soils have lower permeability due to their fine particles.
What affects soil permeability?
Several factors influence soil permeability, including soil texture, structure, organic matter content, compaction, and slope. For example, sandy soils typically have higher permeability than clay soils due to their larger pore spaces, allowing water to flow more freely.
application of permeability of soil
The permeability of soil finds application in various fields, including agriculture, civil engineering, environmental science, and geology. Engineers use knowledge of soil permeability to design drainage systems, assess groundwater flow, and mitigate the impacts of pollution. In agriculture, farmers utilize soil permeability data to optimize irrigation practices and manage soil health for sustainable crop production.
coefficient of permeability of soil
The coefficient of permeability of soil quantifies its permeability and is determined through laboratory tests. The formula for calculating the coefficient of permeability depends on factors such as soil type, pore space, and hydraulic gradient, which represent the slope of water flow. This coefficient provides valuable information for understanding and managing soil permeability in various applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, soil permeability is a crucial aspect of soil health and ecosystem function. By understanding and maintaining soil permeability, we can ensure sustainable water management, support plant growth, preserve soil fertility, and minimize environmental degradation. Whether in agriculture, landscaping, or urban planning, considering soil permeability is essential for fostering a healthy and resilient environment for generations to come.
FAQs
What is soil permeability and why does it matter?
Soil permeability refers to how easily water and other liquids can move through soil. It matters because it influences water management, plant growth, farming success, and environmental sustainability.
How does soil permeability affect plant growth?
Soil permeability directly impacts plant growth by determining how effectively water and nutrients can reach plant roots. If soil is not permeable enough, it can lead to waterlogging or drought stress, hindering plant growth.
Why is soil permeability important for farmers?
Farmers rely on soil permeability for successful crop production. Proper permeability ensures that water and nutrients can penetrate the soil and reach plant roots, resulting in healthier plants and better yields.
What happens if soil isn’t permeable?
If soil isn’t permeable enough, water may pool on the surface, causing waterlogging and root rot. It can also increase erosion and runoff, leading to soil degradation and reduced fertility.
What are the benefits of high soil permeability?
High soil permeability allows water to penetrate quickly, preventing surface runoff and ensuring efficient water distribution to plant roots. It also promotes soil aeration and maintains soil health.
What characteristics make soil good for permeability?
Good permeability soil has a loose, well-aerated structure with plenty of spaces between particles. Sandy soils generally exhibit high permeability due to their larger particle size and better drainage.
What factors influence soil permeability?
Several factors influence soil permeability, including soil texture, structure, compaction, and organic matter content. Sandy soils tend to have higher permeability than clay soils due to their inherent properties.
How is soil permeability measured?
Soil permeability is often measured in the field using methods such as infiltration tests or in the laboratory using instruments like permeameters. These tests assess how quickly water moves through a soil sample under controlled conditions.
How can I improve soil permeability in my garden?
You can improve soil permeability in your garden by incorporating organic matter, such as compost or manure, to improve soil structure and porosity. Avoid excessive compaction and overwatering, which can decrease permeability.
What are some practical applications of soil permeability in everyday life?
Understanding soil permeability is essential for various applications, including agriculture, civil engineering, and environmental science. It helps design irrigation systems, drainage solutions, and infrastructure projects while also guiding land use planning and conservation efforts.