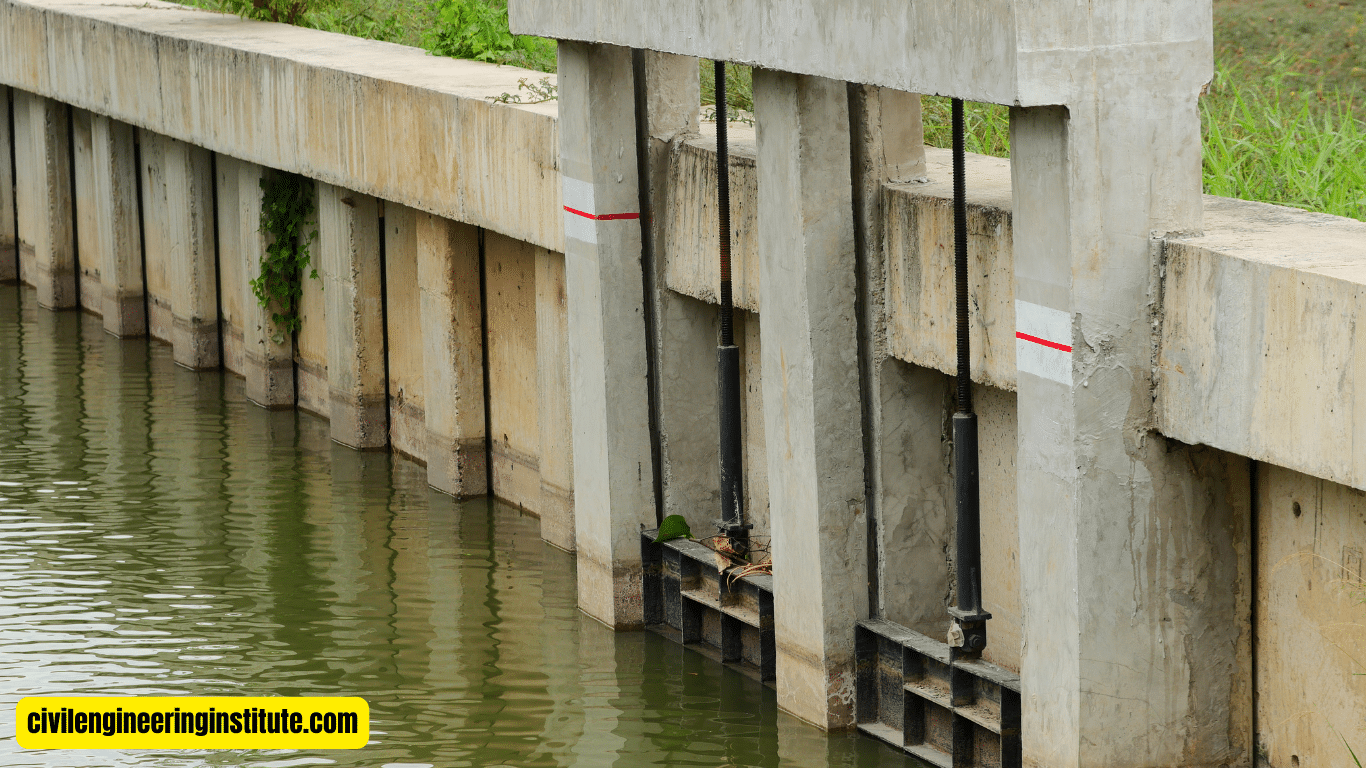
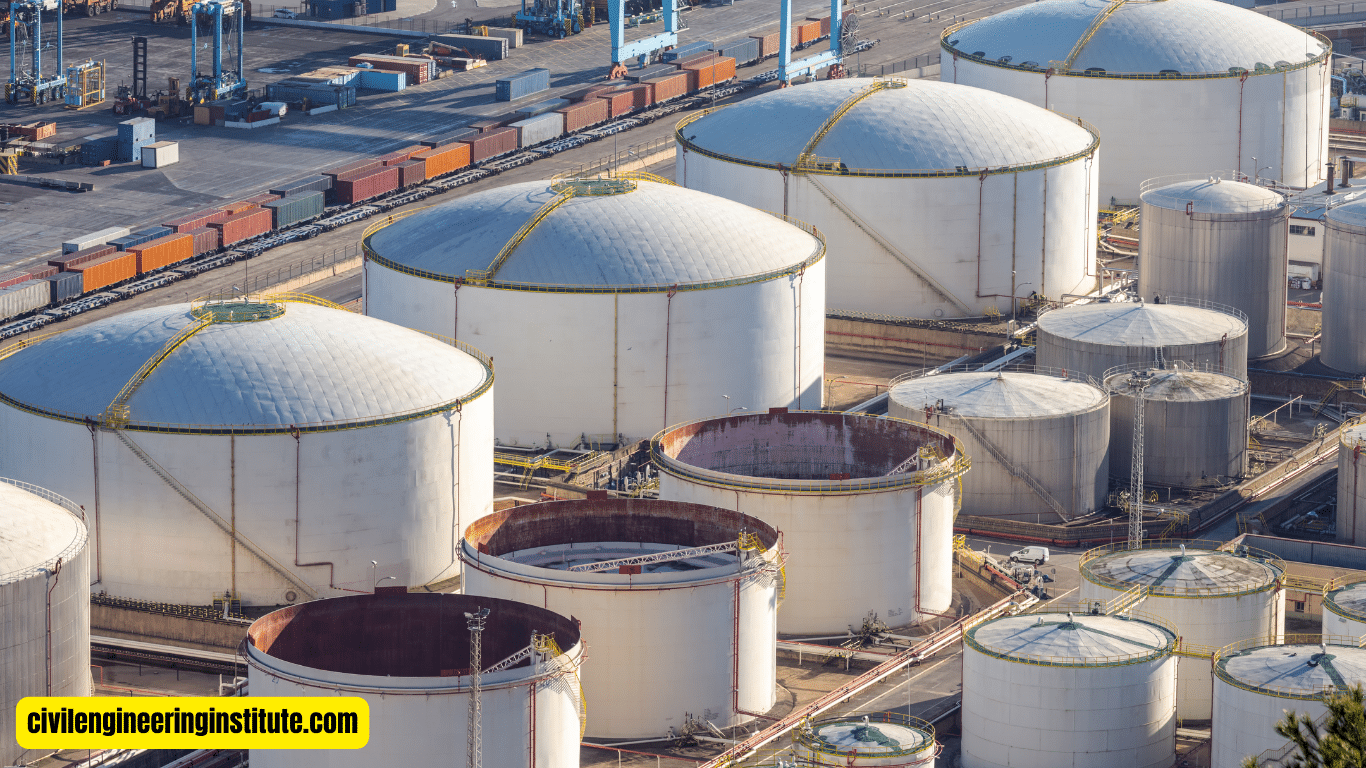
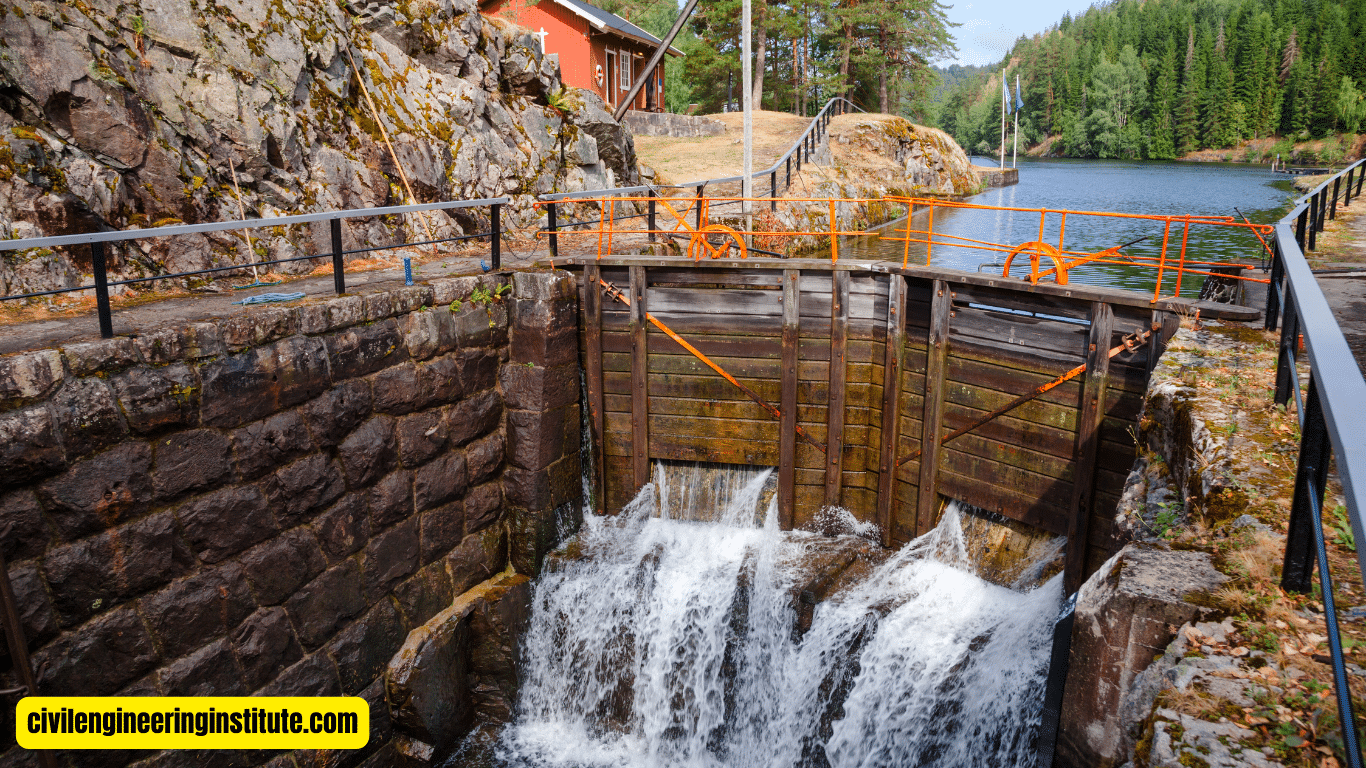
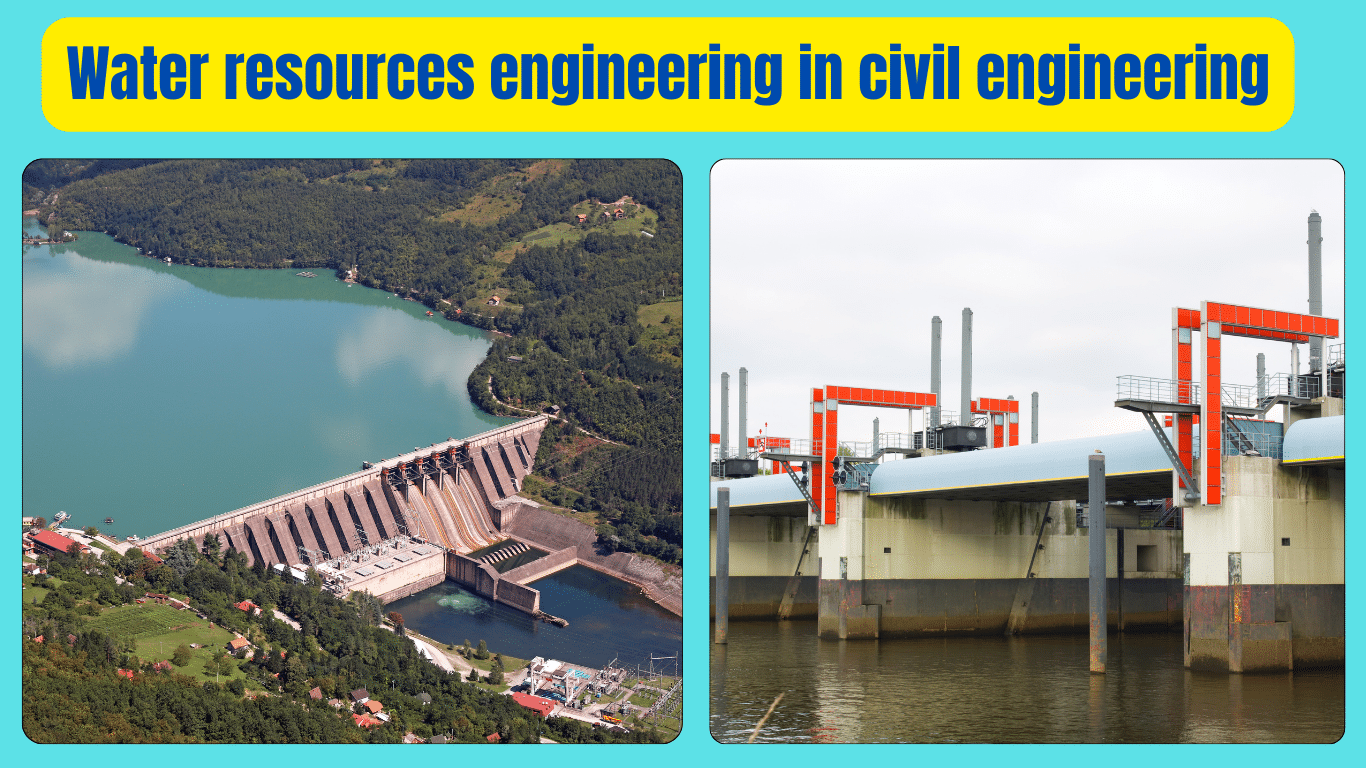
Water resources engineering in civil engineering involves the management, development, and preservation of water-related infrastructure and resources. It plays an important role in ensuring the sustainable use of water for various purposes like irrigation, drinking water supply, hydropower generation, and flood control. Civil engineers specializing in water resources design and maintain systems such as dams, reservoirs, canals, and water treatment plants. They work to ensure that water resources are utilized efficiently while minimizing negative impacts on the environment.
By implementing innovative technologies and strategies, water resources engineers contribute to the conservation of this precious natural resource for current and future generations. Understanding the principles of hydrology, hydraulics, and environmental science, these professionals strive to address the challenges posed by water scarcity, pollution, and climate change. Through their expertise, they aim to create resilient water infrastructure that withstands natural disasters and supports sustainable development.
Water Resources Engineering in Civil Engineering
Water is one of the most vital resources on our planet, essential for sustaining life, supporting ecosystems, and driving various human activities. In the realm of civil engineering, the management and utilization of water resources play a critical role in shaping societies and ensuring sustainable development. Water resources engineering encompasses a wide range of disciplines and practices aimed at effectively managing, conserving, and harnessing water for various purposes.
Understanding the Importance of Water Resources Engineering
Water resources engineering is indispensable for addressing numerous challenges related to water, including scarcity, pollution, and climate change. Civil engineers specializing in this field work tirelessly to develop innovative solutions that optimize water usage, protect the environment, and meet the growing demands of a rapidly expanding global population. By leveraging their expertise in hydrology, hydraulics, and environmental science, water resources engineers play a crucial role in shaping the future of water management and sustainability.
Key Components of Water Resources Engineering
Water resources engineering encompasses a diverse range of components, each serving a unique purpose in the management and utilization of water resources. These components include:
- Hydrology
- Hydraulics
- Water Supply and Distribution
- Wastewater Management
- Flood Control and Management
Hydrology: Hydrology is the study of the distribution, movement, and properties of water on Earth. It involves analyzing rainfall patterns, runoff, infiltration, and evaporation to understand how water behaves within natural and engineered systems. Hydrological studies are essential for predicting floods, assessing water availability, and designing water infrastructure.
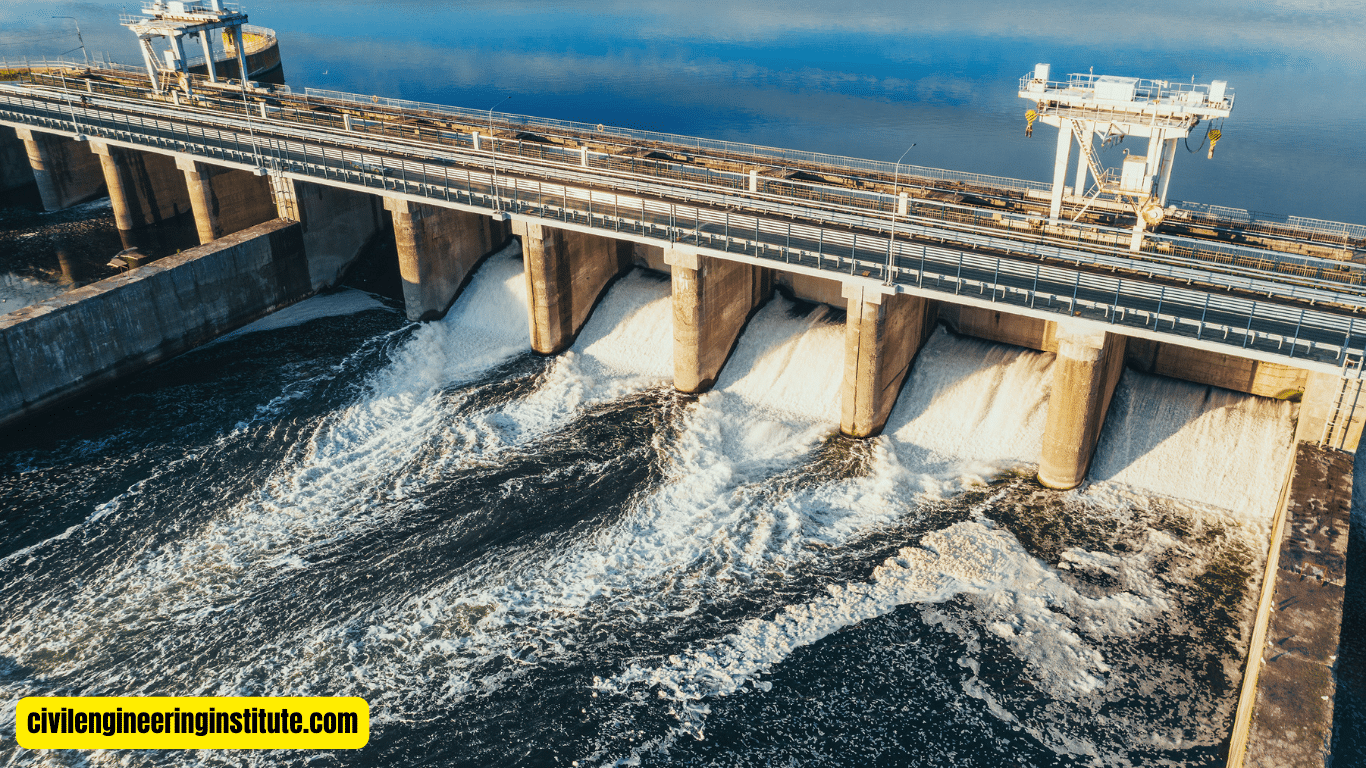
Hydraulics: Hydraulics focuses on the behavior of fluids, particularly water, in motion. In the context of water resources engineering, hydraulics plays a crucial role in designing and analyzing hydraulic structures such as dams, spillways, and channels. Engineers use hydraulic principles to optimize the efficiency and performance of water conveyance systems, ensuring the safe and reliable transport of water.
Water Supply and Distribution: Water supply and distribution involve the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure for delivering clean and safe drinking water to communities. This includes water treatment plants, pipelines, storage reservoirs, and pumping stations. Water resources engineers work to ensure that water supply systems are robust, resilient, and capable of meeting the demands of urban and rural populations.
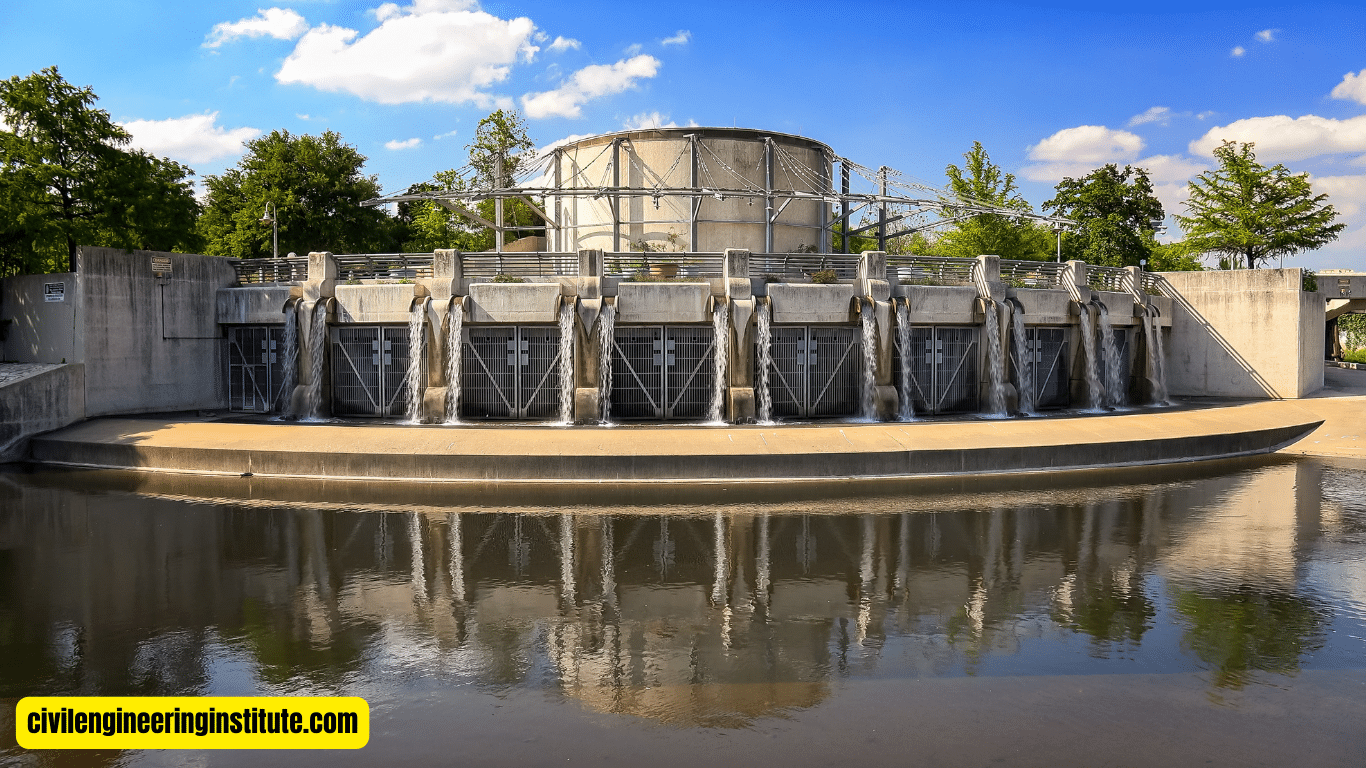
Wastewater Management: Wastewater management is essential for protecting public health and the environment by safely treating and disposing of sewage and industrial effluents. Water resources engineers design wastewater treatment facilities, sewerage systems, and stormwater management systems to minimize pollution and mitigate the impacts of urbanization on water quality.
Flood Control and Management: Flood control and management involve implementing measures to mitigate the risk of flooding and reduce its impact on communities and infrastructure. This includes the construction of levees, floodwalls, and detention basins, as well as the development of flood forecasting and early warning systems. Water resources engineers play a critical role in designing resilient flood control infrastructure that safeguards lives and property from the devastating effects of floods.
Challenges and Opportunities in Water Resources Engineering
Despite the significant advancements in water resources engineering, numerous challenges persist, posing formidable obstacles to sustainable water management. These challenges include:
- Water Scarcity
- Water Pollution
- Climate Change
- Infrastructure Aging
Water Scarcity: With growing population pressures and increasing demands for water across various sectors, water scarcity has emerged as a significant concern in many regions. Water resources engineers are tasked with developing strategies to enhance water conservation, optimize water use efficiency, and explore alternative water sources to alleviate water scarcity.
Water Pollution: Pollution from industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and urban wastewater poses a threat to water quality and ecosystem health. Water resources engineers work to implement pollution control measures, develop innovative wastewater treatment technologies, and promote sustainable land use practices to minimize the impact of pollution on water resources.
Climate Change: Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, exacerbating droughts and floods, and threatening the availability and reliability of water resources. Water resources engineers must adapt to changing climatic conditions by incorporating climate resilience into the design and operation of water infrastructure and implementing measures to mitigate the impacts of climate change on water resources.
Infrastructure Aging: Many water infrastructure systems are aging and in need of repair, rehabilitation, or replacement. Water resources engineers face the challenge of modernizing existing infrastructure to improve efficiency, reliability, and resilience while ensuring the sustainable use of resources and minimizing environmental impacts.
Despite these challenges, water resource engineering also presents numerous opportunities for innovation and advancement. Advances in technology, such as remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS), and computational modeling, enable engineers to gather data, analyze complex systems, and develop predictive tools for more effective water management. Moreover, interdisciplinary collaboration between engineers, scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders is essential for developing holistic solutions that address the multifaceted challenges of water resource management.
Some Key Points: Water resources engineering in civil engineering
Water resources engineering in civil engineering
Water resources in civil engineering refer to the various sources of water that are utilized for different purposes within the realm of civil engineering. These sources include rivers, lakes, groundwater, and rainfall, among others. Civil engineers play a crucial role in managing and harnessing these water resources to meet the needs of society while ensuring sustainability and environmental protection.
The Role of Civil Engineering in the Water Resources Industry
Civil engineering plays a significant role in the water resources industry by designing, constructing, and maintaining infrastructure related to water management and distribution. This includes water treatment plants, dams, reservoirs, pipelines, and irrigation systems. Civil engineers apply their expertise to ensure efficient water supply, effective flood control, and proper wastewater management, thereby contributing to the sustainable use of water resources.
The Function of Water in Civil Engineering
Water serves various functions in civil engineering, ranging from providing drinking water and irrigation for agriculture to supporting industrial processes and generating hydropower. In addition, water plays a critical role in construction activities, such as mixing concrete, controlling dust, and compacting soil. Civil engineers must carefully consider the role of water in different projects and implement measures to manage it effectively.
Water Supply in Civil Engineering
Water supply in civil engineering involves the provision of clean and safe drinking water to communities. Civil engineers design and build water supply systems, including treatment plants, storage tanks, and distribution networks, to ensure reliable access to potable water for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. They also work to address challenges such as water scarcity, contamination, and aging infrastructure to maintain the integrity of water supply systems.
The Use of Water Resources Engineering
Water resources engineering is used to manage and optimize the utilization of water resources for various purposes, including irrigation, hydropower generation, flood control, and environmental conservation. Civil engineers apply principles of hydrology, hydraulics, and environmental science to design and implement sustainable water management strategies that balance the needs of society with the protection of natural ecosystems.
The Four Water Resources
The four main water resources are surface water (such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs), groundwater (water stored underground in aquifers), precipitation (rainfall and snowfall), and desalinated seawater (water that has been treated to remove salt for use as drinking water or irrigation).
Difference Between Water Engineering and Water Resources Engineering
Water engineering focuses on the design and construction of hydraulic structures and systems, such as dams, canals, and pipelines, to manage water resources effectively. On the other hand, water resources engineering involves a broader scope, encompassing the management, conservation, and utilization of water resources for various purposes while considering environmental sustainability and societal needs.
Basics of Water Engineering
The basics of water engineering include understanding the principles of fluid mechanics, hydrology, and hydraulics, as well as the design and operation of water-related infrastructure. Civil engineers apply these fundamentals to analyze water systems, develop engineering solutions, and ensure the efficient management of water resources.
Importance of Water Resources
Water resources are essential for sustaining life, supporting ecosystems, and driving economic development. They provide drinking water, irrigation for agriculture, habitat for wildlife, and energy for hydropower generation. Protecting and managing water resources effectively is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of communities and the sustainability of ecosystems.
Benefits of Water Resources
Effective management of water resources offers numerous benefits, including ensuring reliable access to clean drinking water, supporting agricultural productivity, mitigating the risk of floods and droughts, and promoting economic growth through hydropower generation and recreation. By optimizing the use of water resources, civil engineers contribute to the resilience and prosperity of societies worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, water resources engineering plays a vital role in ensuring the sustainable management and utilization of water resources for the benefit of present and future generations. By integrating scientific knowledge, engineering principles, and innovative technologies, water resources engineers contribute to safeguarding water security, protecting the environment, and promoting human well-being. As we confront the complex challenges posed by water scarcity, pollution, and climate change, the importance of water resource engineering in shaping a more resilient and sustainable water future cannot be overstated. Through collaboration, innovation, and stewardship, we can address these challenges and create a more equitable and resilient water infrastructure that serves the needs of all.
FAQs
What is water resources engineering in civil engineering?
Water resources engineering in civil engineering involves managing, preserving, and utilizing water sources like rivers, lakes, and groundwater for various purposes such as drinking water supply, irrigation, and hydropower generation.
What do water resources engineers do?
Water resources engineers design and build infrastructure like dams, reservoirs, and water treatment plants. They also develop strategies to manage floods, conserve water, and protect the environment.
Why is water resource engineering important?
Water resources engineering is crucial for ensuring sustainable water management, addressing water scarcity, controlling floods, and providing clean drinking water to communities.
What are the main challenges in water resources engineering?
Challenges include water scarcity, pollution, climate change impacts, aging infrastructure, and balancing competing water needs among different users and ecosystems.
How do water resource engineers manage floods?
Water resources engineers design flood control structures like levees, dams, and stormwater management systems. They also develop flood forecasting models and early warning systems.
What is the role of water resources engineering in environmental protection?
Water resources engineering aims to protect natural ecosystems by minimizing pollution, preserving aquatic habitats, and maintaining healthy water flow regimes in rivers and streams.
How do water resource engineers ensure clean drinking water?
Water resources engineers design and operate water treatment plants to remove contaminants from raw water sources and ensure the delivery of safe and clean drinking water to communities.
What is the difference between water resource engineering and water supply engineering?
Water resources engineering focuses on managing overall water availability and quality, while water supply engineering specifically deals with designing and maintaining infrastructure for delivering clean water to consumers.
How does water resource engineering contribute to sustainable development?
Water resources engineering promotes the efficient use of water resources, reduces environmental impacts, supports economic growth through hydropower generation and irrigation, and enhances resilience to climate change.
What skills are needed to become a water resources engineer?
Skills required include knowledge of hydrology, hydraulics, environmental science, engineering design principles, computer modeling, and communication skills for working with diverse stakeholders to address complex water challenges.