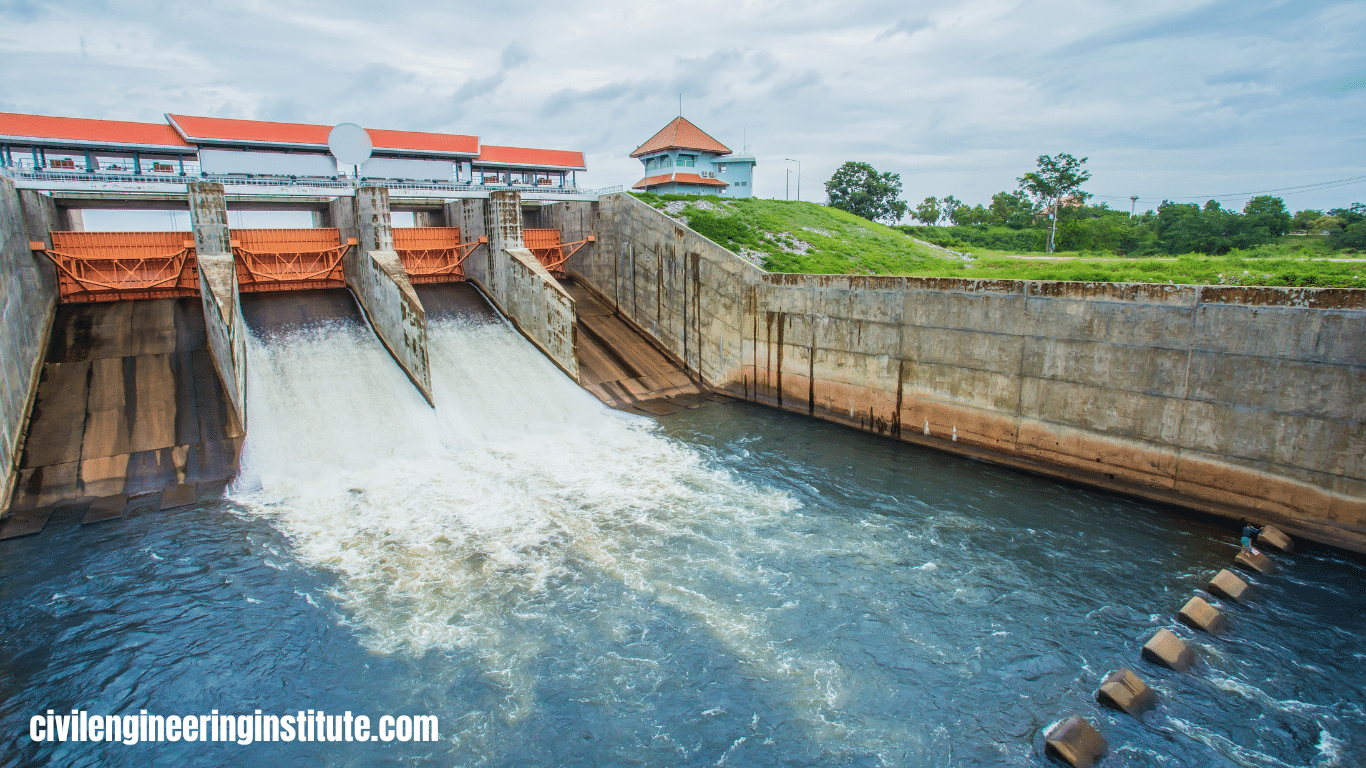
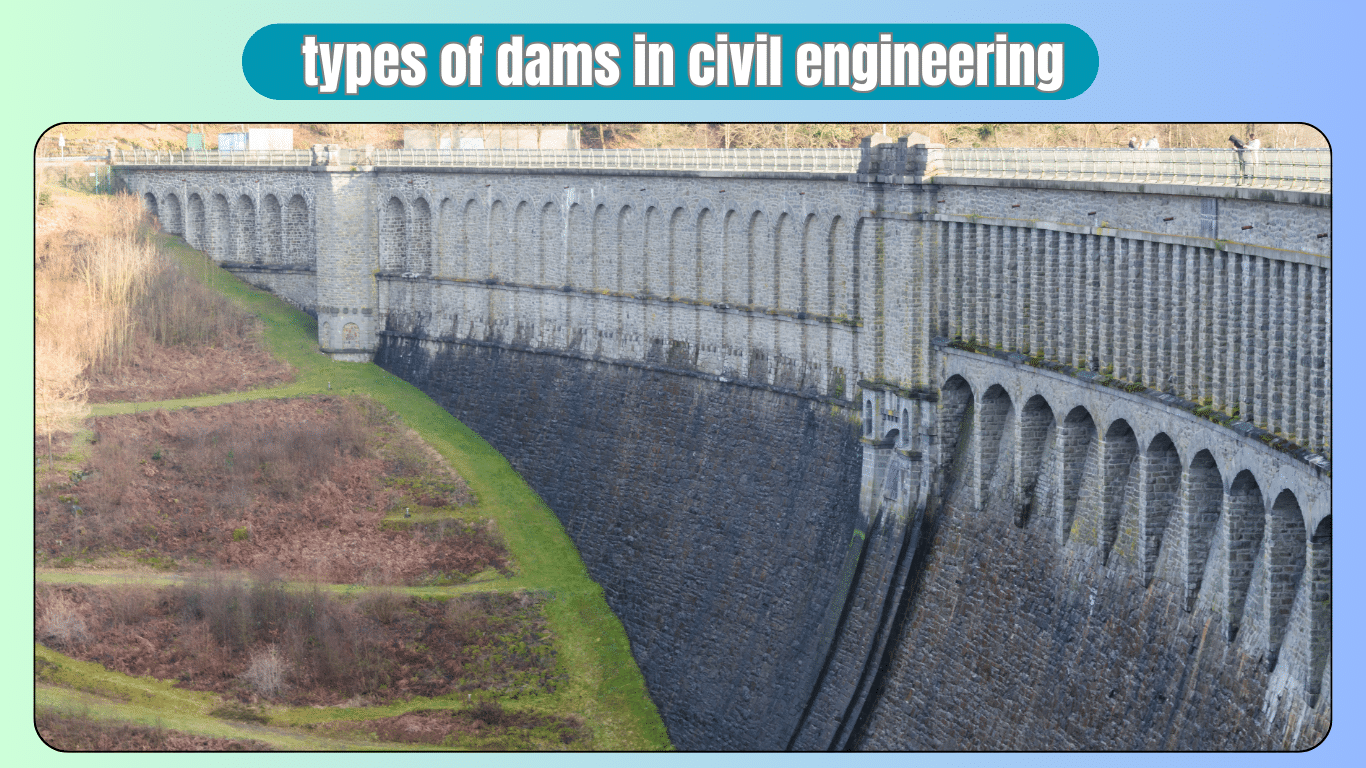
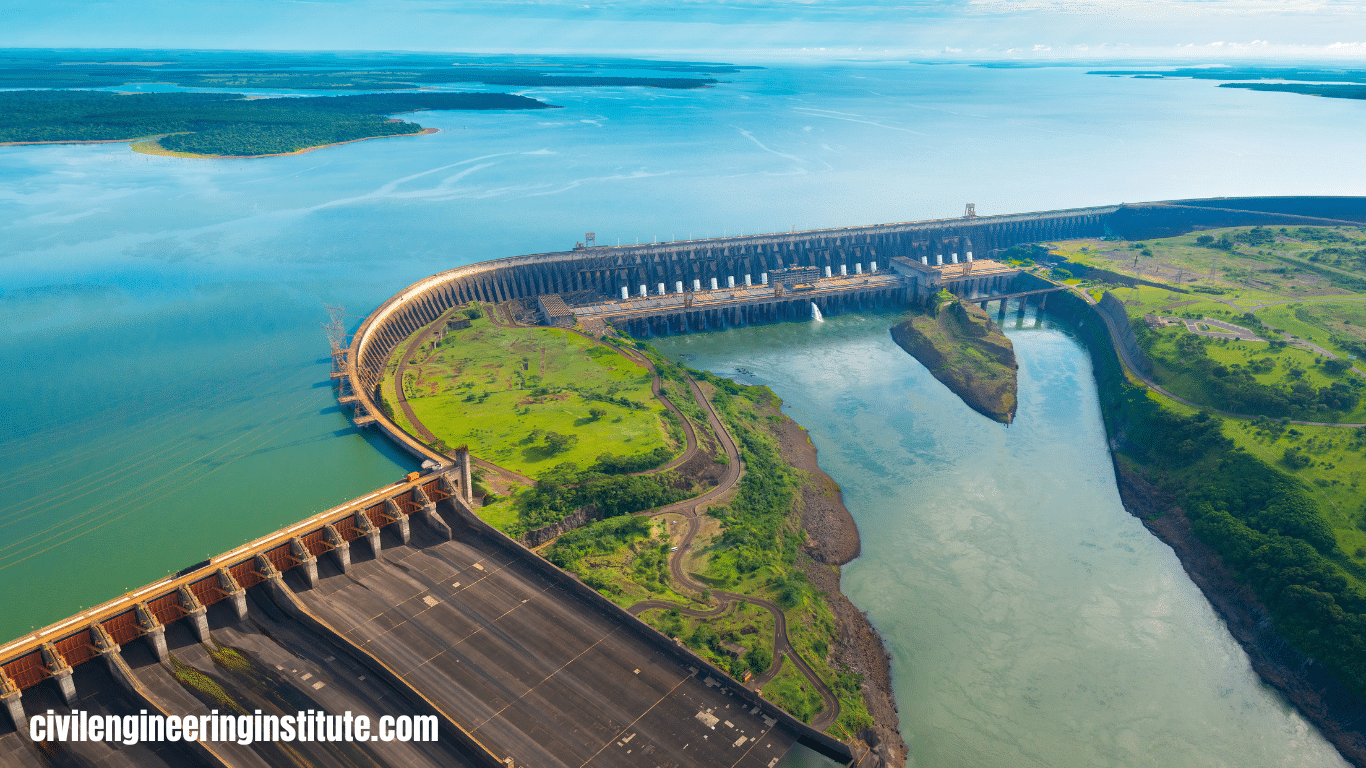
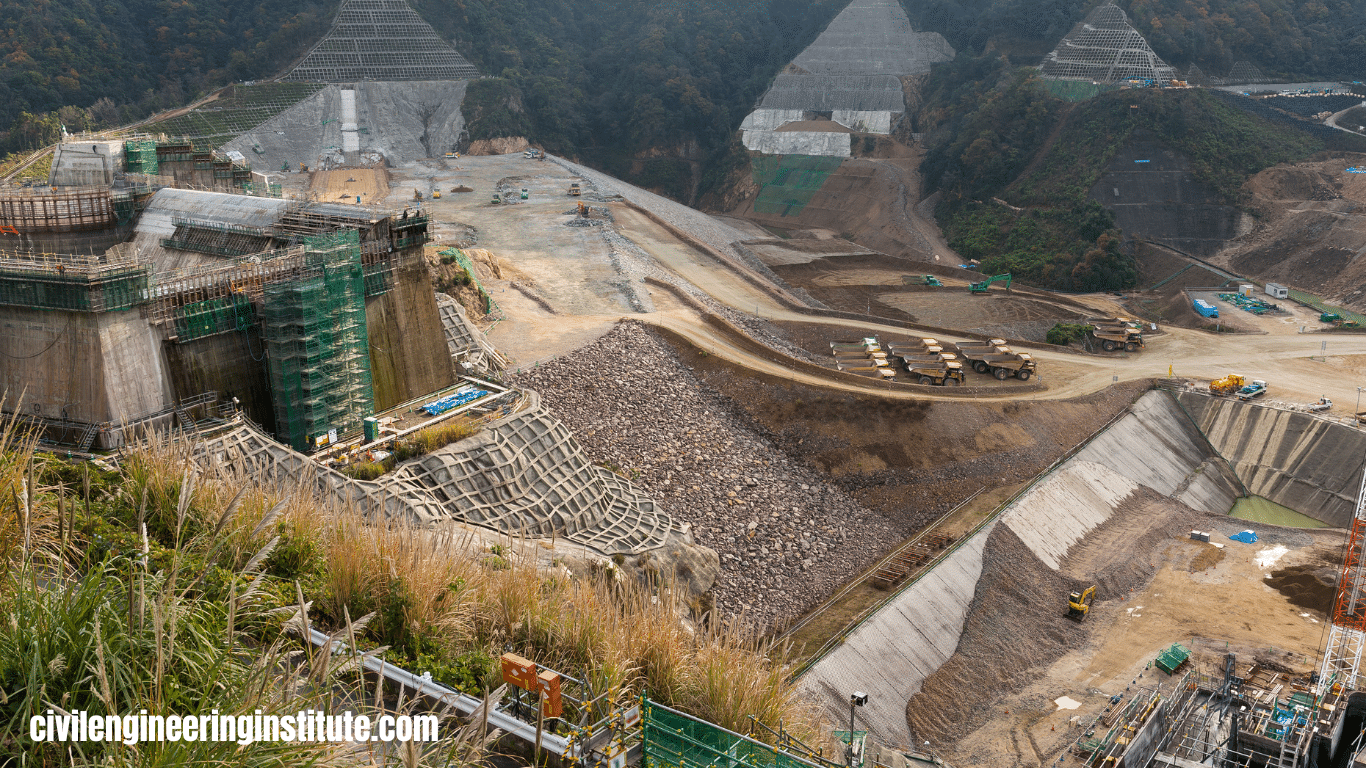
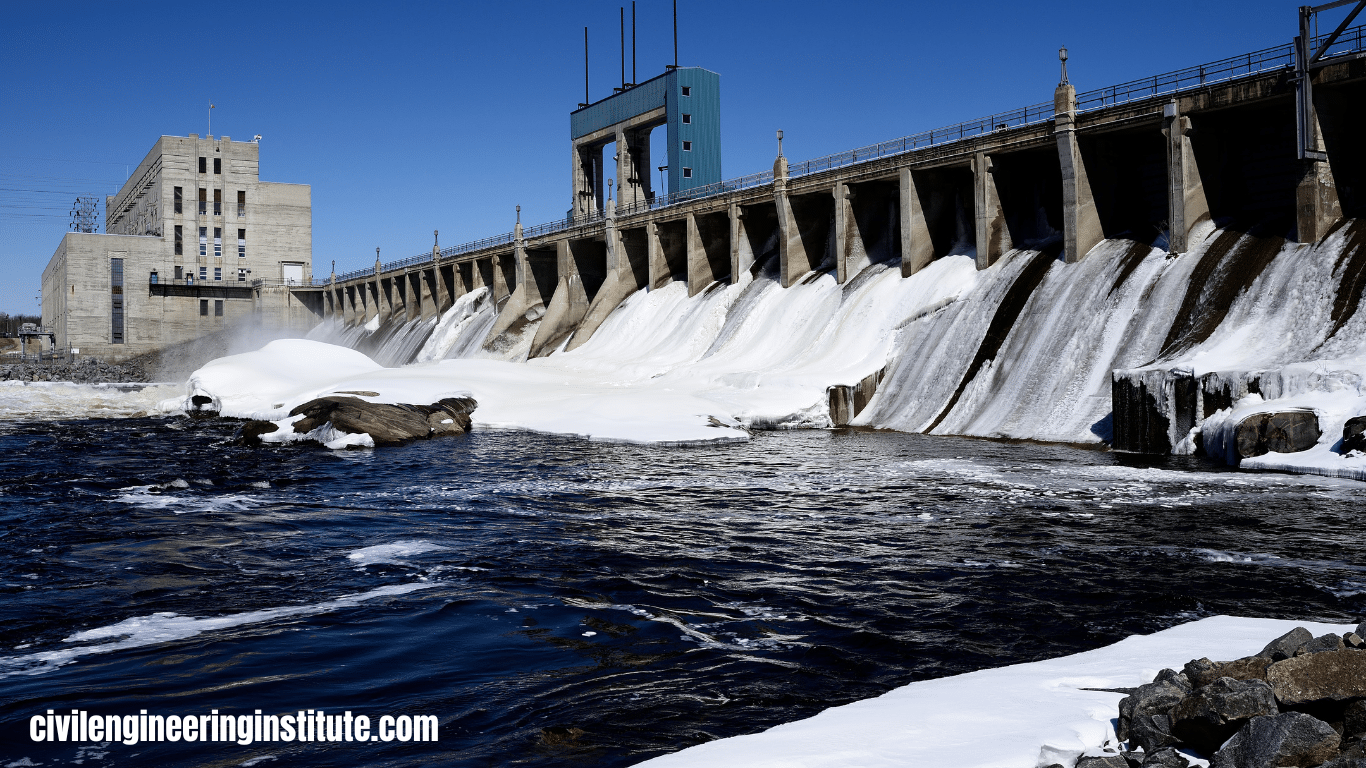
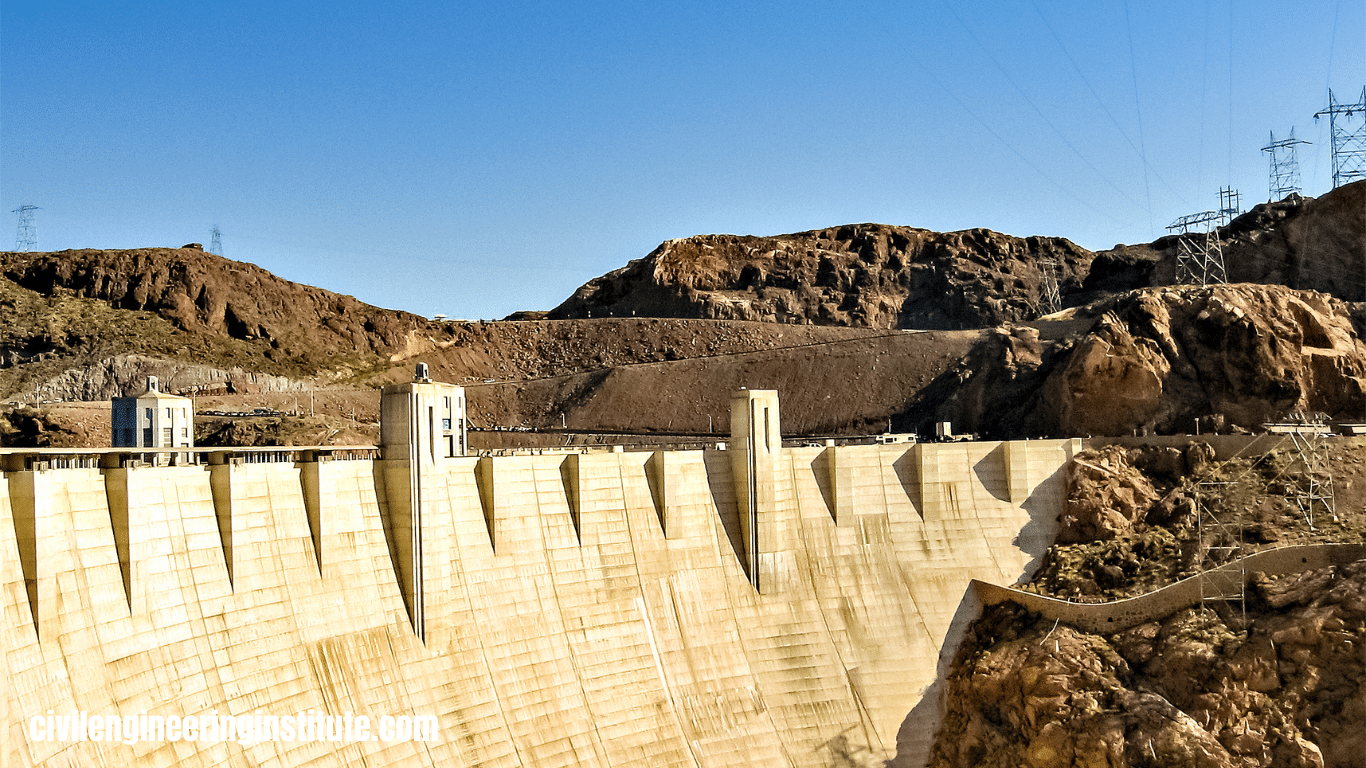
Different types of dams in civil engineering are built to control the flow of water. There are several types of dams used for various purposes. One common type is the gravity dam, which relies on its weight to resist the pressure of water. Another type is the arch dam, which uses the arch shape to distribute water pressure to the sides of the valley.
Then there’s the embankment dam, constructed with earth or rock fill materials. These dams are built to withstand the force of water and serve different needs like irrigation, flood control, and hydroelectric power generation. Each type has its advantages and suitability depending on factors like terrain, water flow, and construction materials.
Types of Dams in Civil Engineering
Dams are essential structures in civil engineering that serve various purposes, including water storage, flood control, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation. They are built across rivers and streams to impound water and create reservoirs. Dams come in different types, each designed to suit specific geological and hydrological conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the various types of dams commonly used in civil engineering projects.
- Gravity Dams
- Arch Dams
- Embankment Dams
Gravity Dams
Gravity dams are among the oldest and most common types of dams. They are constructed using concrete or masonry and rely on their weight to resist the force of water pressure. These dams are typically massive and have a broad base to distribute the water load evenly. Gravity dams are suitable for sites where the bedrock is strong and stable. Examples of gravity dams include Hoover Dam in the United States and the Grand Coulee Dam in Washington.
Arch Dams
Arch dams are curved structures that rely on the arch action to support the reservoir’s water pressure. They are constructed using concrete and are well-suited for narrow canyons or gorges where the abutments can provide lateral support. Arch dams are known for their strength and efficiency in using materials. They require less concrete than gravity dams of similar height. Notable examples of arch dams include the Hoover Dam and the Glen Canyon Dam, both located in the United States.
Embankment Dams
Embankment dams, also known as earthfill dams, are constructed using compacted earth, rock, gravel, and sometimes concrete. These dams are built in areas where locally available materials are abundant. They rely on the weight and internal strength of the fill materials to resist the pressure exerted by the reservoir water. Embankment dams are classified into three main types based on their construction materials and methods:
- Rockfill Dams
- Earthfill Dams
- Composite Dams
- Buttress Dams
- Arch-Gravity Dams
Rockfill Dams
Rockfill dams are built primarily using rock and gravel. They have a watertight core made of impermeable materials such as clay or concrete. The rockfill is placed in layers and compacted to form a stable structure. Rockfill dams are flexible and can adapt to the geological conditions of the site.
Earthfill Dams
Earthfill dams are constructed using compacted earth and clay materials. They are less expensive to build compared to other types of dams and are suitable for sites with ample soil resources. Earthfill dams require careful compaction to ensure stability and prevent water seepage.
Composite Dams
Composite dams combine elements of both concrete and embankment construction. They typically have a concrete core or face supported by embankments on either side. Composite dams are designed to take advantage of the benefits of both materials, providing strength and stability while utilizing locally available fill materials.
Buttress Dams
Buttress dams are characterized by a series of vertical or inclined supports, known as buttresses, that divide the reservoir into compartments. These dams are commonly constructed using reinforced concrete and are suitable for sites with narrow valleys or steep slopes. Buttress dams distribute the water load to the foundation and abutments through the buttresses, providing stability and structural integrity.
Arch-Gravity Dams
Arch-gravity dams combine elements of both arch and gravity dams. They feature a curved upstream face like an arch dam but also utilize the weight of the structure to resist the water pressure, similar to a gravity dam. Arch-gravity dams are well-suited for sites with deep foundations and strong bedrock. They offer a balance between the efficiency of arch dams and the simplicity of gravity dams.
Some key points: Types of dams in civil engineering
What is a Dam?
A dam is a structure built across a river or stream to control the flow of water. It’s like a barrier that holds back the water, creating a reservoir on one side and controlling the release of water on the other.
Different Types of dams in civil engineering
There are several types of dams used in civil engineering, each with its own design and purpose. Some common types include gravity dams, arch dams, and embankment dams. Gravity dams use their weight to resist the force of water; arch dams have a curved shape to distribute water pressure; and embankment dams are made from earth or rock-fill materials.
Classification of Dams in Civil Engineering
Dams can be classified based on various factors like construction materials, design, and purpose. They can be categorized as concrete dams, masonry dams, or earthfill dams, among others. This classification helps engineers determine the most suitable type of dam for a specific location and purpose.
Different Types of Diversion Dams
Diversion dams are designed to redirect the flow of water from its natural course. They can be categorized based on their structure and purpose, such as concrete diversion dams, timber diversion dams, or rockfill diversion dams. These dams play a crucial role in managing water resources for irrigation, water supply, and other purposes.
The Most Common Type of Dam
The most common type of dam is the embankment dam. It is constructed using earth or rock fill materials and is often used for a wide range of purposes, including irrigation, flood control, and hydropower generation. Embankment dams are versatile and can be built on various terrains.
Full Form of Dams
The term “DAM” stands for “Dams and Appurtenant Structures.”. It encompasses not only the dam itself but also any associated structures like spillways, outlets, and powerhouses.
Types of Dam Used for Flood Control
Embankment dams are commonly used for flood control purposes. They can help regulate water flow during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt by storing excess water in the reservoir and releasing it gradually to prevent downstream flooding.
Purpose of Dams in Civil Engineering
The primary purpose of dams in civil engineering is to manage water resources effectively. They are built to provide water supply for irrigation, domestic use, and industrial purposes, generate hydropower, prevent flooding, and improve navigation and recreation opportunities.
Height of a Dam
The height of a dam varies depending on its design and location. Dams can range from a few meters to hundreds of meters in height. The height is usually measured from the foundation level to the crest of the dam.
Dam Measurement
Dam measurement involves assessing various parameters like the height, length, width, and capacity of the reservoir. Engineers use sophisticated instruments and techniques to accurately measure these dimensions and ensure the structural integrity and safety of the dam.
Benefits of a Dam
Dams offer numerous benefits to society and the environment. They help regulate water flow, provide water for irrigation and drinking purposes, generate clean and renewable energy, control floods, improve navigation, create recreational opportunities, and support biodiversity by creating habitats for aquatic species. However, it’s essential to consider potential environmental and social impacts and manage dams sustainably to maximize their benefits while minimizing negative consequences.
Conclusion
Dams are critical infrastructure components that play a vital role in water resource management and development. Understanding the different types of dams and their characteristics is essential for engineers and planners involved in dam construction projects. Whether it’s harnessing hydropower, ensuring water supply, or mitigating flood risks, selecting the appropriate dam type is crucial to achieving project objectives effectively and sustainably. Each type of dam has its advantages and limitations, and careful consideration of geological, hydrological, and environmental factors is necessary to ensure the success and longevity of dam structures.
FAQs
What are the different types of dams in civil engineering?
The different types of dams include gravity dams, arch dams, and embankment dams, each serving specific purposes and constructed with different designs.
How do gravity dams differ from arch dams?
Gravity dams rely on their weight to resist the force of water, while arch dams use the arch shape to distribute water pressure to the sides of the valley.
What is the classification of dams based on construction materials?
Dams can be classified based on construction materials such as concrete dams, masonry dams, or earthfill dams, aiding engineers in choosing the most suitable type for a particular location and purpose.
Which type of dam is commonly used for hydropower generation?
Embankment dams are commonly used for hydropower generation due to their versatility and ability to hold back large volumes of water.
What are the advantages of embankment dams?
Embankment dams are advantageous because they can be built in various terrains, they are cost-effective, and they provide flexibility in design and construction.
How are diversion dams classified based on structure?
Diversion dams are classified based on structure, including concrete diversion dams, timber diversion dams, or rockfill diversion dams, each serving to redirect the flow of water from its natural course.
What is the most suitable type of dam for flood control?
Embankment dams are commonly used for flood control purposes because they can regulate water flow by storing excess water in the reservoir and releasing it gradually to prevent downstream flooding.
Can you explain the design differences between concrete and masonry dams?
Concrete dams are constructed using poured concrete, while masonry dams are built using individual blocks or stones held together with mortar. Concrete dams are more suitable for larger structures and high-pressure conditions.
What factors determine the height of a dam?
The amount of water a dam must hold, the local topography, and engineering considerations related to stability and safety all affect the height of the structure.
What are the environmental considerations when choosing a dam type?
Environmental considerations include the impact on wildlife habitats, water quality, downstream flow regimes, and the potential for sedimentation. Choosing the right dam type involves balancing engineering needs with environmental concerns to minimize negative impacts.