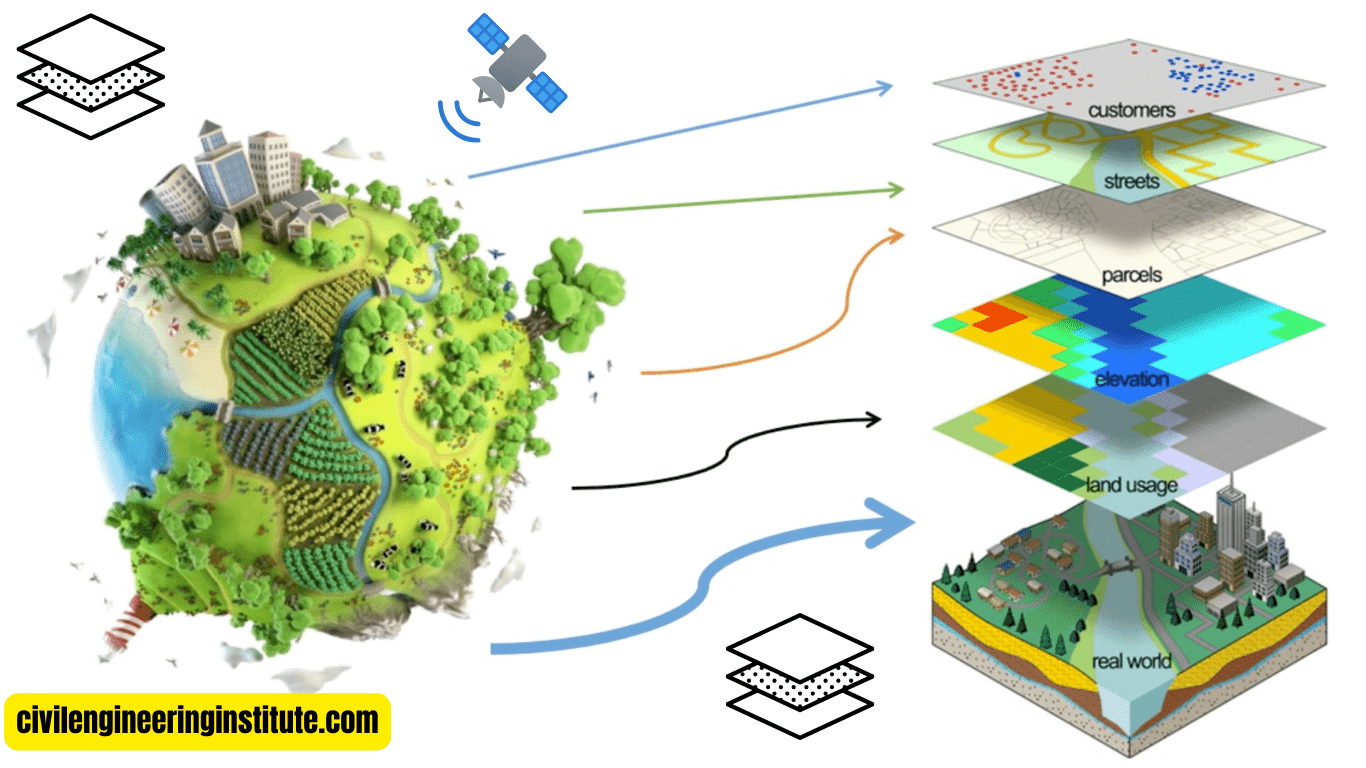
Image acquisition in GIS process is an essential step, involving the collection of visual data for mapping and analysis. In simple terms, it’s like taking pictures from above to understand and manage our world better. This process uses various methods, such as aerial photography, satellite imagery, and drones, to capture images of the Earth’s surface.
These images provide valuable information about land use, vegetation, urban development, and more. By optimizing the acquisition process, GIS professionals ensure high-quality data for accurate mapping and decision-making. It’s like having a bird’s-eye view of the Earth, helping us study and protect our environment effectively.
Understanding Image Acquisition in GIS: A Beginner’s Guide
In the realm of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), image acquisition stands as a pivotal process, enabling the collection of visual data crucial for mapping, analysis, and decision-making. This article aims to delve into the fundamentals of image acquisition within the GIS framework, offering insights into its significance, methods, and applications.
What is Image Acquisition?
At its core, image acquisition involves the capture of visual data representing the Earth’s surface through various techniques, such as aerial photography, satellite imagery, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones. These images serve as essential inputs for GIS, providing valuable information on land use, terrain characteristics, environmental changes, and more.
The Significance of Image Acquisition in GIS
Image acquisition plays a vital role in GIS applications across diverse fields, including urban planning, agriculture, natural resource management, disaster response, and environmental monitoring. By acquiring high-quality images, GIS professionals can create accurate maps, analyze spatial patterns, and derive actionable insights to address complex challenges.
Methods of Image Acquisition
- Aerial Photography
- Satellite Imagery
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
Aerial Photography: is a traditional method involving the use of aircraft equipped with cameras to capture images of the Earth’s surface. Aerial photography offers high-resolution imagery suitable for detailed mapping and analysis.
Satellite Imagery: Utilizing satellites orbiting the Earth, satellite imagery provides a broader perspective of large areas. With advancements in satellite technology, high-resolution and multispectral imagery are readily available, enabling a wide range of GIS applications.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Also known as drones, UAVs have emerged as versatile tools for image acquisition in GIS. Equipped with cameras and remote sensing devices, drones can capture imagery with high spatial resolution, making them ideal for localized mapping and monitoring.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, image acquisition in GIS poses several challenges and considerations. These include:
- Cost
- Data Processing
- Weather Conditions
Cost: Acquiring high-quality imagery, especially through aerial photography and satellite services, can incur significant costs. Organizations must weigh the benefits against the expenses to ensure cost-effective solutions.
Data Processing: Raw image data acquired through various methods requires processing to extract meaningful information. This involves image rectification, georeferencing, and analysis, necessitating specialized skills and software.
Weather Conditions: Weather conditions such as cloud cover, haze, and precipitation can hinder image acquisition, affecting the quality and usability of the captured imagery. Timing and seasonal variations must be considered to optimize data collection efforts.
Applications of Image Acquisition in GIS
- Urban Planning and Development
- Environmental Monitoring
- Precision Agriculture
- Disaster Response and Management
Urban Planning and Development: Image acquisition enables urban planners to assess land use patterns, infrastructure development, and demographic trends, facilitating informed decision-making for sustainable urban growth.
Environmental Monitoring: By capturing images of natural landscapes and ecosystems, GIS professionals can monitor environmental changes, habitat degradation, and biodiversity loss, aiding conservation efforts and ecosystem management.
Precision Agriculture: In agriculture, image acquisition facilitates crop monitoring, yield estimation, and pest detection through the analysis of vegetation indices and thermal imagery. This enables farmers to optimize resource allocation and enhance crop productivity.
Disaster Response and Management: During natural disasters such as floods, wildfires, and earthquakes, image acquisition provides timely and accurate information for assessing damages, identifying vulnerable areas, and coordinating relief efforts.
Future Trends in Image Acquisition
The field of image acquisition in GIS is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in technology and a growing demand for spatial data solutions. Future trends include:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Advancements in Remote Sensing Technologies
- Expansion of UAV Applications
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are increasingly being employed to automate image processing tasks such as feature extraction, classification, and change detection, streamlining GIS workflows and enhancing efficiency.
Advancements in Remote Sensing Technologies: Ongoing advancements in remote sensing technologies, including hyperspectral imaging, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and synthetic aperture radar (SAR), are expanding the capabilities of image acquisition in GIS, enabling more detailed and accurate data collection.
Expansion of UAV Applications: The use of drones for image acquisition is expected to grow across various industries, driven by improvements in UAV capabilities, regulatory frameworks, and cost-effectiveness. This trend will democratize access to spatial data and empower organizations with localized insights.
Some important key points: Image acquisition in GIS process
Steps in Image Processing in GIS
Image processing in GIS involves several steps to transform raw imagery into meaningful data for analysis and visualization. These steps typically include preprocessing, enhancement, classification, and interpretation.
Steps of Image Acquisition
The steps of image acquisition encompass the process of capturing visual data from the Earth’s surface using various methods such as aerial photography, satellite imagery, and drones. These steps involve planning the acquisition, capturing the images, and ensuring data quality through calibration and validation.
Function of Image Acquisition
The primary function of image acquisition is to collect visual data representing the Earth’s surface, which serves as essential input for Geographic Information Systems (GIS). This data enables the creation of accurate maps, analysis of spatial patterns, and decision-making in diverse fields such as urban planning, agriculture, and environmental management.
Example of Image Acquisition
An example of image acquisition is the use of satellite imagery to monitor deforestation in the Amazon rainforest. Satellites capture images of the forest canopy over time, allowing researchers to track changes in vegetation cover, identify deforested areas, and assess the impact of human activities on the ecosystem.
Different Types of GIS Images
GIS images can be classified into various types based on their source, resolution, and spectral characteristics. Common types include aerial photographs, satellite imagery, LiDAR data, and thermal infrared imagery. Each type of image serves specific purposes and applications in GIS analysis.
Image Acquisition and Its Techniques
Image acquisition refers to the process of capturing visual data from the Earth’s surface using techniques such as aerial photography, satellite imaging, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). These techniques employ different sensors and platforms to collect imagery with varying spatial and spectral resolutions.
Image Configuration in Remote Sensing
Image configuration in remote sensing involves adjusting various parameters such as spatial resolution, spectral bands, and radiometric calibration to optimize the quality and usability of acquired imagery. This ensures that the images accurately represent the features and phenomena of interest on the Earth’s surface.
Conclusion
In conclusion, image acquisition serves as a fundamental component of the GIS process, enabling the collection of visual data essential for spatial analysis, mapping, and decision-making. By understanding the methods, challenges, and applications of image acquisition, organizations and professionals can harness its potential to address complex challenges and drive innovation in diverse fields. As technology continues to advance, image acquisition in GIS will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the world and guiding informed actions for a sustainable future.
FAQs
What is image acquisition in GIS?
Image acquisition in GIS is the process of capturing visual data about the Earth’s surface using methods like aerial photography and satellite imagery.
Why is image acquisition important in GIS?
Image acquisition is crucial in GIS as it provides the necessary data for creating accurate maps, analyzing landscapes, and making informed decisions.
What are the methods used for image acquisition in GIS?
Methods for image acquisition in GIS include aerial photography, satellite imagery, and drones equipped with cameras.
How are images captured in image acquisition?
Images are captured using specialized cameras mounted on aircraft, satellites orbiting the Earth, or drones flying over specific areas.
What kinds of information can be gathered through image acquisition in GIS?
Image acquisition in GIS can gather information on land use, vegetation cover, urban development, environmental changes, and more.
Can anyone access images acquired in GIS?
Yes, many organizations provide access to acquired images through online platforms or specialized databases for research and analysis purposes.
Are there any challenges in image acquisition?
Challenges in image acquisition include weather conditions affecting image quality, cost considerations, and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
How is image quality ensured in GIS image acquisition?
Image quality is ensured through processes like calibration, validation, and quality control measures to maintain accuracy and reliability.
What are the benefits of using drones for image acquisition in GIS?
Drones offer benefits such as flexibility, high spatial resolution, and the ability to capture images in hard-to-reach or hazardous areas.
How does image acquisition contribute to environmental management?
Image acquisition in GIS aids environmental management by providing data for monitoring deforestation, assessing habitat changes, and studying climate impacts on landscapes.