How to use geographic information systems is a basic question for engineers. (GIS) are powerful tools used to analyze, visualize, and interpret spatial data. To begin using GIS, you first need to understand its basic principles. Start by gathering your geographic data, which could include anything from maps to satellite images. Next, input this data into your GIS software. Once your data is loaded, you can begin to explore and manipulate it. This might involve overlaying different layers of information to identify patterns or trends.
GIS allows you to perform various analyses, such as determining the best location for a new store or mapping out areas prone to natural disasters. Additionally, GIS enables you to create visually appealing maps and presentations to communicate your findings effectively. With practice and experimentation, you’ll become proficient in using GIS to solve spatial problems and make informed decisions.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
In today’s data-driven world, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as indispensable tools for analyzing, interpreting, and visualizing spatial data. Whether you’re a seasoned GIS professional or a newcomer to the field, understanding how to effectively utilize GIS can greatly enhance your ability to make informed decisions and solve complex spatial problems. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of GIS and provide practical tips on how to harness its full potential.
Understanding Geographic Information Systems
At its core, GIS is a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing geographic data. It allows users to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and present spatial or geographic data. This data can range from maps and satellite imagery to demographic information and environmental data. By integrating various data layers and performing spatial analyses, GIS enables users to gain valuable insights into geographic patterns, relationships, and trends.
Getting Started with GIS
Before diving into GIS, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with its basic components and functionalities. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Acquiring Geographic Data
- Choosing the Right Software
- Loading Data into GIS
Acquiring Geographic Data: The first step in using GIS is acquiring the necessary geographic data. This data can be obtained from a variety of sources, including government agencies, commercial vendors, and open data repositories. Common types of geographic data include aerial imagery, topographic maps, census data, and satellite imagery.
Choosing the Right Software: Once you have acquired your geographic data, the next step is to choose the right GIS software for your needs. There are many GIS software options available, ranging from open-source platforms like QGIS to proprietary solutions like ArcGIS. Consider factors such as cost, functionality, and ease of use when selecting GIS software.
Loading Data into GIS: After selecting your GIS software, it’s time to load your geographic data into the software. Most GIS software allows you to import various types of data, including shapefiles, raster images, and GPS data. Once your data is loaded, you can begin exploring and analyzing it using the tools and functionalities provided by the software.
Exploring GIS Functionality
Now that you have your geographic data loaded into GIS, it’s time to explore the various functionalities and tools available to you. Here are some key features of GIS that you should familiarize yourself with:
- Spatial Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Geocoding and Georeferencing
- Network Analysis
Spatial Analysis: One of the primary capabilities of GIS is spatial analysis, which allows you to perform various analytical tasks on your geographic data. This can include tasks such as overlaying different layers of data to identify spatial relationships, conducting proximity analysis to determine the nearest features, and performing spatial statistics to analyze patterns and trends.
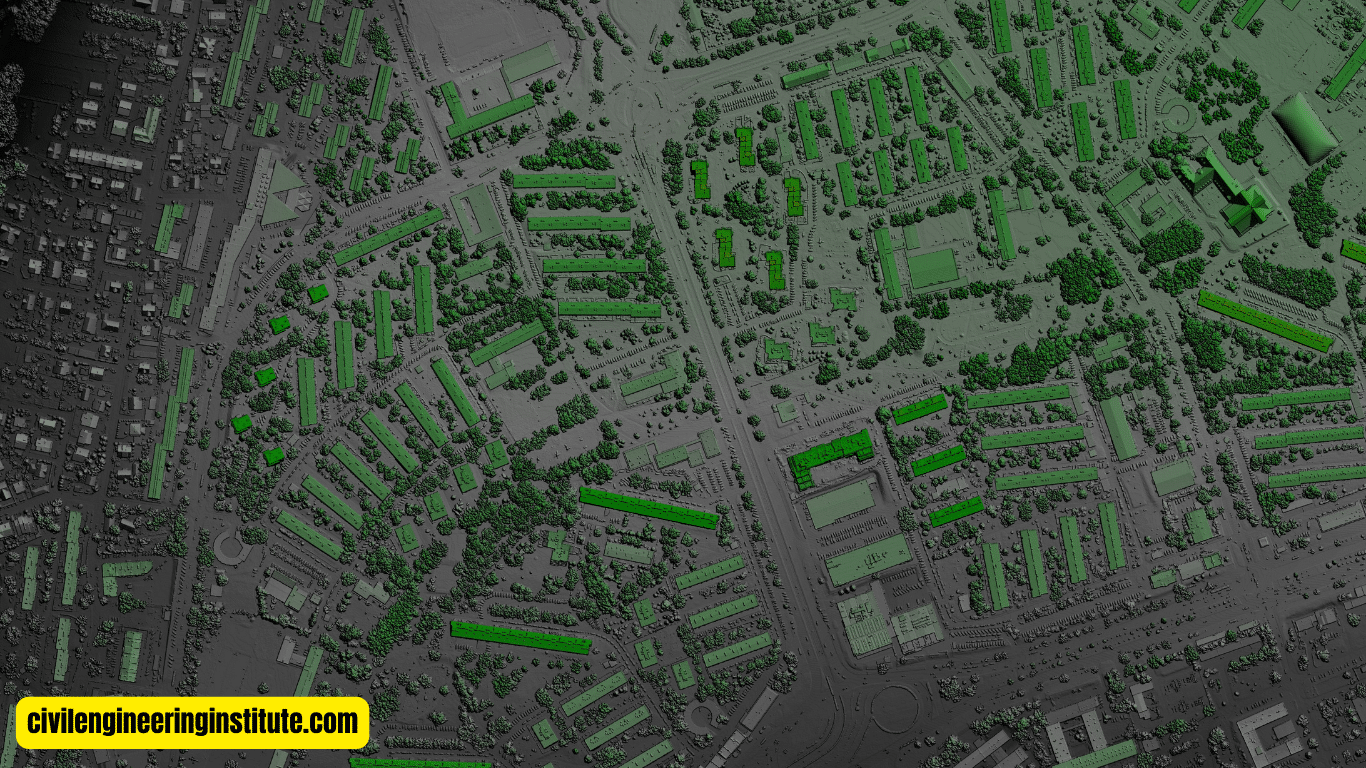
Data Visualization: GIS provides powerful tools for visualizing geographic data in the form of maps, charts, and graphs. You can customize the appearance of your maps by adjusting colors, symbols, and labels to effectively communicate your findings.
Geocoding and Georeferencing: GIS enables you to geocode and georeference data, which involves assigning geographic coordinates to addresses or locations and aligning raster images with geographic coordinates, respectively. This allows you to accurately locate and display data on a map.
Network Analysis: GIS software often includes tools for conducting network analysis, which involves analyzing the flow of goods, services, or information through a network of interconnected features. This can be useful for tasks such as route optimization, facility location analysis, and transportation planning.
Practical Applications of GIS
GIS has a wide range of practical applications across various industries and domains. Here are some examples of how GIS is used in real-world scenarios:
- Urban Planning
- Natural Resource Management
- Disaster Management
- Public Health
Urban Planning: Urban planners use GIS to analyze land use patterns, assess environmental impacts, and plan infrastructure projects such as roads, utilities, and public transportation systems.
Natural Resource Management: GIS is used in natural resource management to monitor and manage forests, wetlands, watersheds, and wildlife habitats. It helps conservationists make informed decisions about land use, habitat restoration, and biodiversity conservation.
Disaster Management: GIS plays a crucial role in disaster management by helping emergency responders assess risk, plan evacuation routes, and allocate resources during natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires.
Public Health: Public health officials use GIS to analyze disease outbreaks, track the spread of infectious diseases, and identify areas with limited access to healthcare services. GIS helps policymakers develop targeted interventions and allocate resources to address public health challenges.
Tips for Success in GIS
As you embark on your journey with GIS, here are some tips to help you succeed:
- Continuous Learning
- Practice Hands-On
- Collaborate with Others
- Attention to Detail
Continuous Learning: GIS is a vast and evolving field, so it’s essential to stay updated on the latest developments, technologies, and best practices. Take advantage of online courses, tutorials, and webinars to expand your knowledge and skills.
Practice hands-on: The best way to learn GIS is by doing. Take on projects that challenge you to apply your GIS skills to real-world scenarios. Practice working with different types of data and experimenting with various analytical techniques.
Collaborate with Others: GIS is often a collaborative endeavor, so don’t hesitate to reach out to fellow GIS professionals for advice, feedback, and collaboration opportunities. Join online forums, attend conferences, and participate in local GIS user groups to connect with others in the field.
Attention to Detail: Pay close attention to detail when working with geographic data, as small errors or inaccuracies can have significant consequences. Double-check your data inputs, perform quality assurance checks, and document your workflows to ensure reproducibility and accuracy.
Some important key points: How to use geographic information systems
How do I use geographic information systems?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used in various ways to analyze and interpret spatial data. One common use is in urban planning, where GIS helps city planners assess land use patterns, plan infrastructure projects, and make decisions about zoning and development. For example, GIS can be used to determine the best locations for new schools, parks, or public transportation routes by analyzing factors such as population density, traffic patterns, and environmental considerations. In environmental science, GIS is used to monitor and manage natural resources, track changes in land cover, and assess the impact of human activities on ecosystems.
Additionally, GIS is used in disaster management to map risk areas, plan evacuation routes, and coordinate emergency response efforts during natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires. Overall, GIS is a versatile tool that can be applied to a wide range of fields and industries to solve complex spatial problems and make informed decisions.
What is the scope of GIS?
The scope of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is vast and encompasses a wide range of applications across various industries and domains. In urban planning and development, GIS is used to analyze land use patterns, assess infrastructure needs, and plan for sustainable growth. In environmental science and natural resource management, GIS is used to monitor and manage forests, wetlands, watersheds, and wildlife habitats.
GIS is also used in agriculture to optimize crop production, manage irrigation systems, and analyze soil health. In public health, GIS is used to track the spread of infectious diseases, identify high-risk areas, and plan healthcare interventions. Additionally, GIS has applications in transportation planning, disaster management, archaeology, telecommunications, and many other fields. The scope of GIS is continually expanding as new technologies and data sources become available, making it an essential tool for decision-making and problem-solving in the modern world.
Is GIS a useful skill?
Yes, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a highly useful skill that is in demand across various industries and sectors. Proficiency in GIS can open up a wide range of career opportunities in fields such as urban planning, environmental science, public health, agriculture, transportation, and emergency management.
Employers value candidates who have GIS skills because it enables them to analyze spatial data, make informed decisions, and solve complex problems. GIS professionals are in high demand in both the public and private sectors, including government agencies, consulting firms, research institutions, and nonprofit organizations. Whether you’re interested in mapping urban landscapes, studying ecosystems, or analyzing demographic trends, GIS skills can help you stand out in the job market and advance your career.
What do geographic information systems (GIS) bring to us?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) bring a multitude of benefits to individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. One of the primary benefits of GIS is its ability to facilitate informed decision-making by providing valuable insights into spatial relationships, patterns, and trends. GIS enables users to analyze complex data sets, identify spatial patterns, and visualize information in a way that is easy to understand and communicate.
This, in turn, helps organizations and policymakers make better decisions about land use planning, resource management, disaster preparedness, and public health interventions. Additionally, GIS promotes collaboration and information sharing by providing a common platform for storing, accessing, and analyzing geographic data. By harnessing the power of GIS, we can better understand the world around us, address pressing challenges, and create more sustainable and resilient communities.
What are some interesting uses of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used in a wide range of interesting and innovative ways across various industries and sectors. One fascinating use of GIS is in archaeology, where it is used to map archaeological sites, analyze spatial relationships between artifacts, and reconstruct ancient landscapes.
GIS is also used in wildlife conservation to track animal movements, identify critical habitat areas, and plan conservation efforts. In transportation planning, GIS is used to analyze traffic patterns, optimize transportation routes, and plan for future infrastructure projects. Additionally, GIS is used in sports analytics to analyze player performance, track game statistics, and optimize team strategies. These are just a few examples of the diverse and exciting applications of GIS that highlight its versatility and potential to transform how we understand and interact with the world around us.
Conclusion
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offer a powerful set of tools for analyzing, interpreting, and visualizing spatial data. By mastering the fundamentals of GIS and exploring its various functionalities, you can unlock valuable insights into geographic patterns, relationships, and trends. Whether you’re an urban planner, environmental scientist, or public health official, GIS can help you make informed decisions and solve complex spatial problems. So, roll up your sleeves, dive into GIS, and let the journey begin!
FAQs
What is GIS, and how does it work?
GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, which are computer-based tools used to analyze and visualize geographic data. They work by integrating various layers of geographic information to create maps and perform spatial analysis.
What kind of data can I use with GIS?
You can use a wide range of data with GIS, including maps, satellite images, aerial photographs, demographic information, and environmental data.
Do I need special software to use GIS?
Yes, you’ll need GIS software to work with geographic data. There are both free and paid options available, such as QGIS, ArcGIS, and Google Earth.
Can I use GIS for personal projects?
Absolutely! GIS can be used for personal projects like planning hiking routes, mapping your neighborhood, or visualizing your travel experiences.
How do I learn to use GIS?
There are many resources available to learn GIS, including online tutorials, courses, and workshops. You can also practice by experimenting with GIS software and exploring available datasets.
What kinds of analyses can I perform with GIS?
With GIS, you can perform various analyses, such as spatial queries, buffering, overlay analysis, proximity analysis, and network analysis.
Is GIS only used by professionals?
Even though professionals in fields like urban planning, environmental science, and public health frequently use GIS, anyone can learn to use it for personal or professional projects.
Can GIS help me find directions?
Yes, GIS can be used for navigation and finding directions. Many mapping applications and GPS devices use GIS technology to provide directions and route planning.
Is GIS useful for business purposes?
Yes, GIS can be incredibly useful for businesses in areas like site selection, market analysis, logistics planning, and customer segmentation.
Are there any limitations to using GIS?
While GIS is a powerful tool, it does have limitations. These may include the availability and quality of data, the complexity of analysis, and the need for specialized skills to use advanced features.