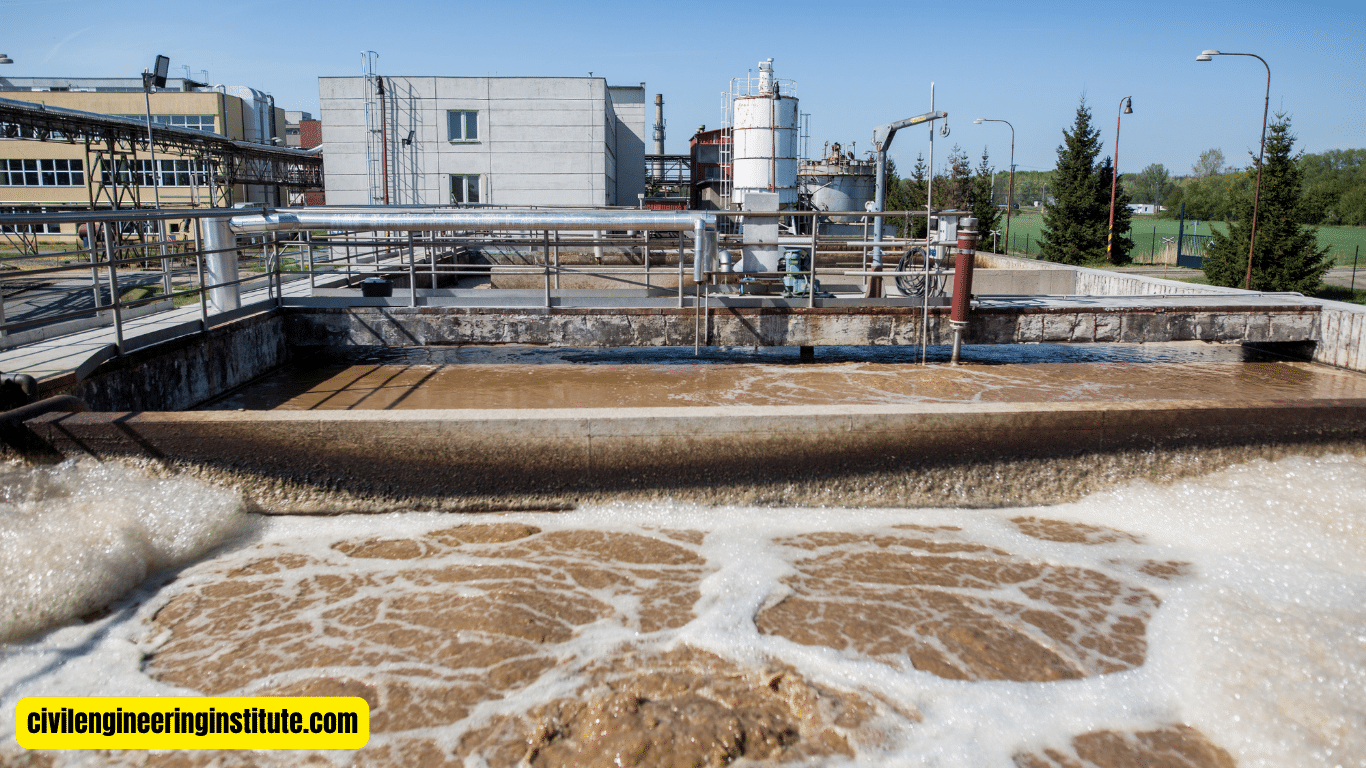
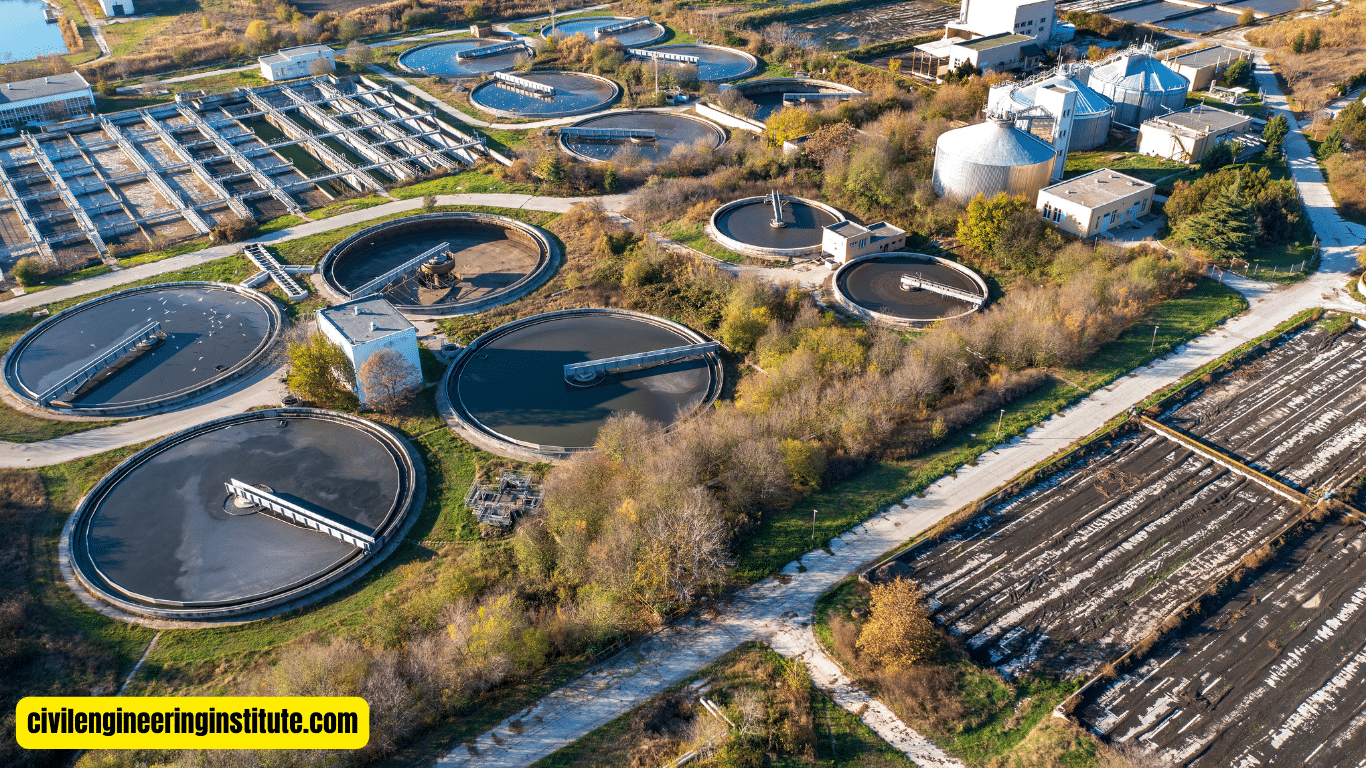
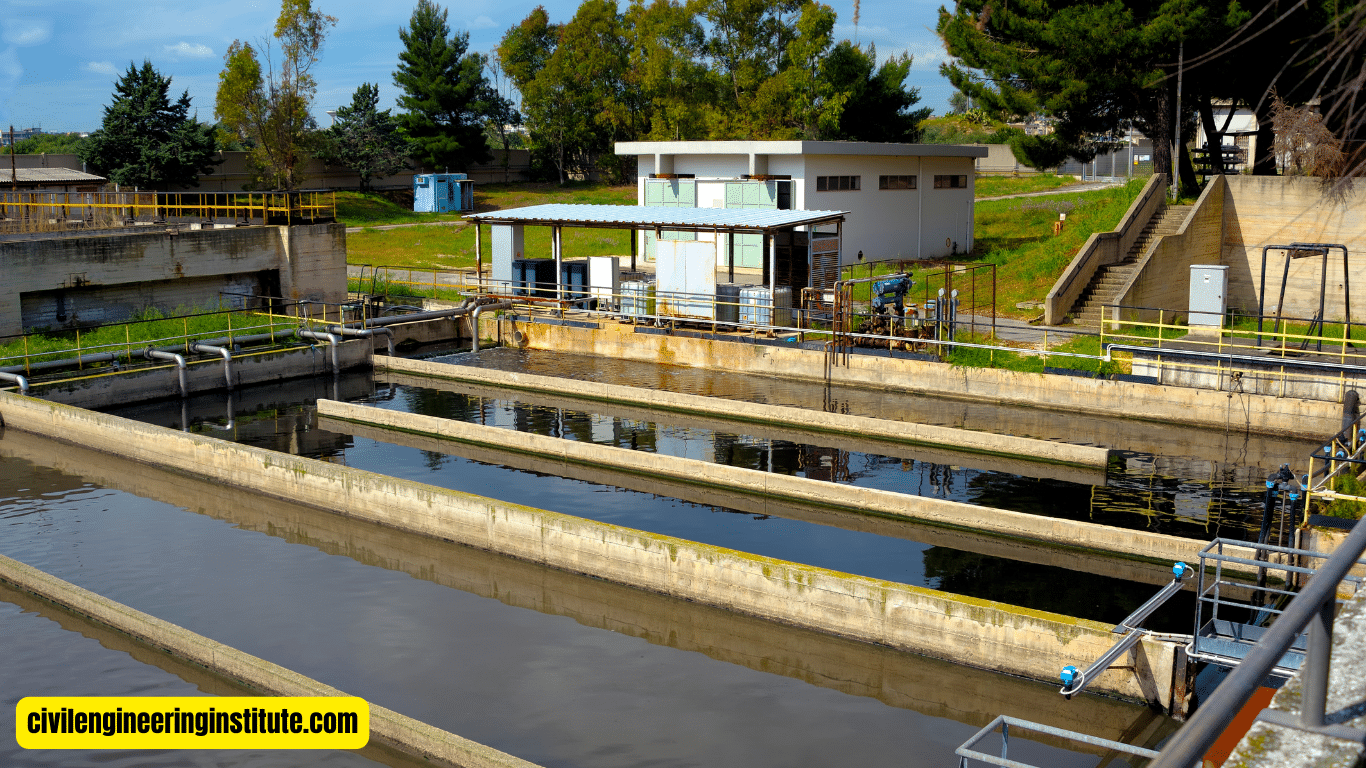
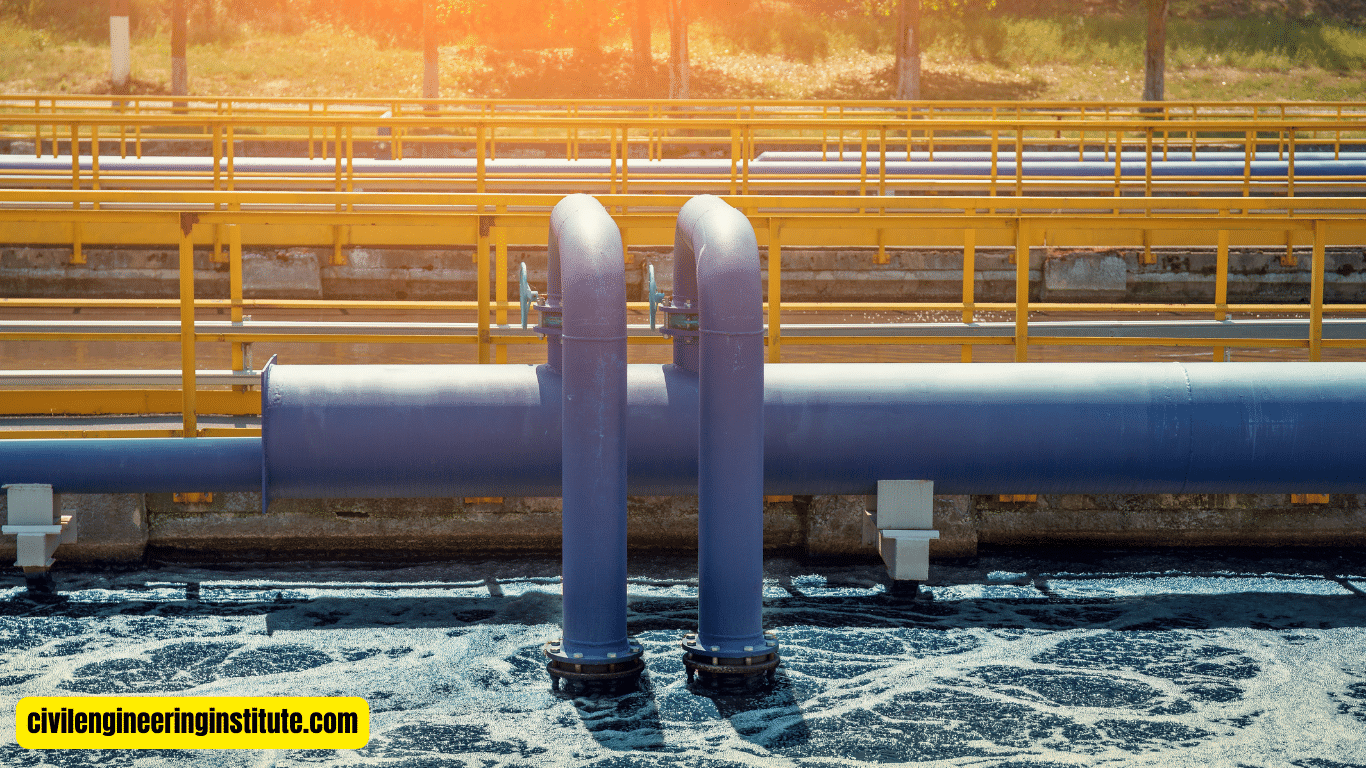
To effectively use activated sludge design, start by understanding its basics. Activated sludge is a biological wastewater treatment process that relies on microorganisms to break down organic matter. To begin, assess your wastewater treatment needs and calculate the appropriate size for your activated sludge system. Next, ensure proper aeration and mixing in the treatment tank to promote microbial growth and activity.
Monitor key parameters, such as dissolved oxygen levels, sludge volume, and nutrient concentrations, regularly to maintain optimal conditions. Additionally, consider factors like hydraulic retention time and sludge age to fine-tune the efficiency of your system. Regular maintenance, including sludge wasting and periodic system checks, is crucial for sustained performance. By following these steps and continuously optimizing your activated sludge design, you can effectively treat wastewater and achieve the desired environmental outcomes.
Understanding How to use activated sludge design
Activated sludge design is a crucial aspect of wastewater treatment, playing a vital role in purifying water before it is released back into the environment. This process involves the use of microorganisms to break down organic matter present in wastewater, effectively removing harmful pollutants and contaminants. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of activated sludge design, exploring how it works and providing practical tips on its implementation.
How to use activated sludge design?
Activated sludge treatment works through a series of biological and chemical reactions that occur within a treatment tank. Wastewater is introduced into the tank, where it comes into contact with a culture of microorganisms known as activated sludge. These microorganisms feed on the organic matter present in the wastewater, breaking it down into simpler compounds such as carbon dioxide and water. The process also involves the aeration of the wastewater, which provides oxygen to the microorganisms and promotes their growth and activity.
Key Components of Activated Sludge Design
Several key components are essential for the successful implementation of activated sludge design:
- Treatment Tank
- Aeration System
- Clarifier
- Return Sludge Pump
Treatment Tank: The treatment tank is where the activated sludge process takes place. It is typically a large, rectangular, or circular structure equipped with mechanisms for aeration and mixing.
Aeration System: Aeration is a critical aspect of activated sludge design, as it ensures that the microorganisms have an adequate supply of oxygen to carry out their metabolic processes. Aeration systems typically consist of diffusers or aerators that introduce air into the wastewater.
Clarifier: After the activated sludge has undergone treatment, it is separated from the treated wastewater in a clarifier. The clarifier allows the activated sludge to settle to the bottom of the tank, where it can be recycled back into the treatment process.
Return Sludge Pump: The return sludge pump is responsible for returning a portion of the settled sludge from the clarifier back into the treatment tank. This helps maintain a stable population of microorganisms within the system.
Designing an Activated Sludge System
Designing an activated sludge system requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure its effectiveness and efficiency.
- Wastewater Characteristics
- Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT)
- Sludge Age
- Aeration Rate
Wastewater Characteristics: The characteristics of the wastewater being treated, such as its flow rate, organic content, and nutrient levels, play a significant role in the design of the activated sludge system. Analyzing these characteristics is essential for determining the size and capacity of the treatment tank, as well as the aeration requirements.
Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT): HRT refers to the amount of time that wastewater spends in the treatment tank during the activated sludge process. It is a critical parameter that influences the efficiency of the treatment process. A longer HRT allows for more extensive treatment of the wastewater but may require a larger tank size.
Sludge Age: Sludge age refers to the average amount of time that microorganisms remain in the treatment system before being wasted or removed. Maintaining an appropriate sludge age is essential for ensuring the health and activity of the microbial population. Too short of a sludge age may result in incomplete treatment, while too long of a sludge age can lead to the accumulation of inert solids.
Aeration Rate: The rate at which air is introduced into the treatment tank affects the growth and activity of the microorganisms. Proper aeration is crucial for maintaining optimal conditions for microbial metabolism. Factors such as the type of aeration system used and the depth of the tank influence the required aeration rate.
Tips for Optimizing Activated Sludge Design
Optimizing activated sludge design involves fine-tuning various parameters to achieve the desired level of wastewater treatment.
- Monitor Key Parameters
- Maintain Proper Mixing
- Implement Nutrient Removal
- Practice Regular Maintenance
Monitor Key Parameters: Regular monitoring of key parameters such as dissolved oxygen levels, sludge volume, and nutrient concentrations is essential for ensuring the effectiveness of the treatment process. By tracking these parameters, operators can identify any issues or inefficiencies and take corrective action promptly.
Maintain Proper Mixing: Adequate mixing of the wastewater within the treatment tank is essential for ensuring uniform distribution of oxygen and nutrients to the microorganisms. Proper mixing helps prevent the formation of dead zones where treatment may be incomplete.
Implement Nutrient Removal: In addition to removing organic matter, activated sludge systems can also be designed to remove nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater. This process, known as nutrient removal, helps prevent eutrophication of receiving water bodies and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Practice Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the activated sludge system is crucial for preventing equipment failures and ensuring long-term reliability. This includes tasks such as sludge wasting, equipment inspection, and calibration of monitoring instruments.
Some basic queries: How to use activated sludge design
How Can Activated Sludge be Used?
Activated sludge is a highly versatile method used for treating wastewater in various industries and municipalities. It is employed to remove organic matter, suspended solids, and harmful contaminants from wastewater, making it safe for discharge into the environment. Activated sludge systems are commonly found in wastewater treatment plants where they play a crucial role in purifying large volumes of wastewater efficiently. Additionally, activated sludge can be utilized in smaller-scale applications, such as onsite septic systems, to treat domestic wastewater before it is released into the soil.
Design of Activated Sludge System
The design of an activated sludge system involves careful consideration of several factors to ensure its effectiveness and efficiency. Key components include a treatment tank, aeration system, clarifier, and return sludge pump. The size and capacity of the treatment tank are determined based on the characteristics of the wastewater being treated, including flow rate and organic content. Hydraulic retention time (HRT), sludge age, and aeration rate are critical parameters that influence the design of the system and its performance.
How to Calculate Activated Sludge
Calculating activated sludge involves determining the appropriate size and capacity of the treatment tank based on the characteristics of the wastewater and desired treatment goals. Engineers and wastewater treatment specialists use mathematical models and empirical data to estimate parameters such as hydraulic retention time, sludge age, and aeration requirements. These calculations help ensure that the activated sludge system is properly designed to achieve the desired level of treatment efficiency.
Methodology of Activated Sludge Process
The activated sludge process involves introducing wastewater into a treatment tank containing a culture of microorganisms known as activated sludge. The microorganisms feed on organic matter present in the wastewater, breaking it down into simpler compounds through biological and chemical reactions. Aeration is provided to the tank to supply oxygen to the microorganisms, promoting their growth and activity. After treatment, the activated sludge is separated from the treated wastewater in a clarifier and recycled back into the treatment process.
Types of Activated Sludge
There are four main types of activated sludge systems: conventional activated sludge, extended aeration, sequencing batch reactor (SBR), and membrane bioreactor (MBR). Each type has its own unique characteristics and is suited to different wastewater treatment applications based on factors such as treatment goals, space constraints, and effluent quality requirements.
Major Components of Activated Sludge
The three major components of activated sludge are the treatment tank, aeration system, and clarifier. The treatment tank is where the activated sludge process takes place, while the aeration system provides oxygen to the microorganisms. The clarifier separates the treated wastewater from the activated sludge, allowing the sludge to settle and be recycled back into the treatment process.
Why is it Called Activated Sludge?
Activated sludge is called so because the microorganisms present in the treatment process are in an “activated” state, meaning they are actively metabolizing and breaking down organic matter in the wastewater. The term “sludge” refers to the biomass that forms as a result of microbial growth and activity in the treatment tank.
Advantages of Activated Sludge
Activated sludge offers several advantages as a wastewater treatment method, including high treatment efficiency, flexibility in design and operation, and the ability to remove a wide range of pollutants and contaminants from wastewater. Additionally, activated sludge systems can be cost-effective and require relatively simple maintenance compared to other treatment technologies.
Depth of Activated Sludge Process
The depth of the activated sludge process varies depending on the specific design of the treatment system and the desired treatment goals. In general, treatment tanks are designed to provide sufficient depth to allow for proper mixing and aeration of the wastewater while ensuring that the settling of the activated sludge occurs effectively in the clarifier.
Efficiency of Activated Sludge Process
The efficiency of the activated sludge process depends on various factors, including the characteristics of the wastewater, design of the treatment system, and operational parameters such as hydraulic retention time and sludge age. When properly designed and operated, activated sludge systems can achieve high levels of treatment efficiency, effectively removing organic matter and pollutants from wastewater.
Disadvantages of Sludge
While activated sludge offers numerous advantages, there are also some disadvantages associated with sludge management. These include the need for proper disposal or treatment of the excess sludge generated during the treatment process, potential odor and aesthetic concerns, and the risk of sludge-related environmental impacts if not managed properly.
How Does an Activated Sludge System Work for Wastewater Treatment Plants?
In wastewater treatment plants, activated sludge systems work by treating large volumes of wastewater using a combination of biological and chemical processes. Wastewater is introduced into a treatment tank containing activated sludge, where it undergoes biological treatment to remove organic matter and contaminants. Aeration is provided to the tank to promote microbial growth and activity, while settling in a clarifier separates the treated wastewater from the activated sludge. The sludge is then recycled back into the treatment process, completing the treatment cycle.
Benefits of Using the Activated Sludge Process in Wastewater Treatment
The activated sludge process offers numerous benefits for wastewater treatment, including high treatment efficiency, flexibility in design and operation, and the ability to remove a wide range of pollutants and contaminants from wastewater. Additionally, activated sludge systems can be cost-effective and require relatively simple maintenance compared to other treatment technologies, making them suitable for a variety of wastewater treatment applications.
Formation of Activated Sludge
Activated sludge is formed through the growth and proliferation of microorganisms in the treatment tank. These microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, feed on organic matter present in the wastewater, forming a dense biomass known as activated sludge. The sludge is kept “activated” through continuous aeration and mixing, allowing for efficient treatment of the wastewater.
Difference Between Activated Sludge and Biological Treatment
While both activated sludge and biological treatment involve the use of microorganisms to treat wastewater, there are some key differences between the two processes. Activated sludge specifically refers to a suspended growth process where microorganisms are kept in suspension in the treatment tank. Biological treatment, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses various treatment methods, including attached growth processes such as trickling filters and rotating biological contactors. Each method has its advantages and is suited to different wastewater treatment applications based on factors such as treatment goals, space constraints, and effluent quality requirements.
Conclusion
Activated sludge design is a fundamental aspect of wastewater treatment, providing an effective and environmentally friendly solution for purifying wastewater. By understanding the principles of activated sludge design and implementing best practices, operators can optimize the performance of their treatment systems and achieve consistently high-quality effluent. With proper design, monitoring, and maintenance, activated sludge systems can play a vital role in protecting public health and preserving the integrity of our natural water resources.
FAQs
What is activated sludge design?
Activated sludge design refers to the process of planning and implementing systems that use microorganisms to treat wastewater effectively.
How does activated sludge work?
Activated sludge works by introducing microorganisms into wastewater, where they consume organic matter and harmful contaminants, purifying the water.
What are the key components of activated sludge design?
The key components include a treatment tank, aeration system, clarifier, and return sludge pump.
How do you calculate activated sludge?
Activated sludge is calculated based on factors such as wastewater characteristics, hydraulic retention time, and sludge age.
What are the advantages of activated sludge?
Advantages include high treatment efficiency, flexibility, and the ability to remove a wide range of pollutants from wastewater.
Why is it called activated sludge?
It’s called activated because the microorganisms are in an active state, breaking down organic matter in the wastewater.
What are the disadvantages of activated sludge?
Disadvantages include the need for proper sludge management, potential odor concerns, and environmental impacts if not managed correctly.
What is the depth of the activated sludge process?
The depth varies based on design and treatment goals, ensuring proper mixing and settling of sludge in the clarifier.
How efficient is the activated sludge process?
When properly designed and operated, activated sludge systems can achieve high levels of treatment efficiency.
How is activated sludge formed?
Activated sludge is formed through the growth and proliferation of microorganisms in the treatment tank, feeding on organic matter in the wastewater.