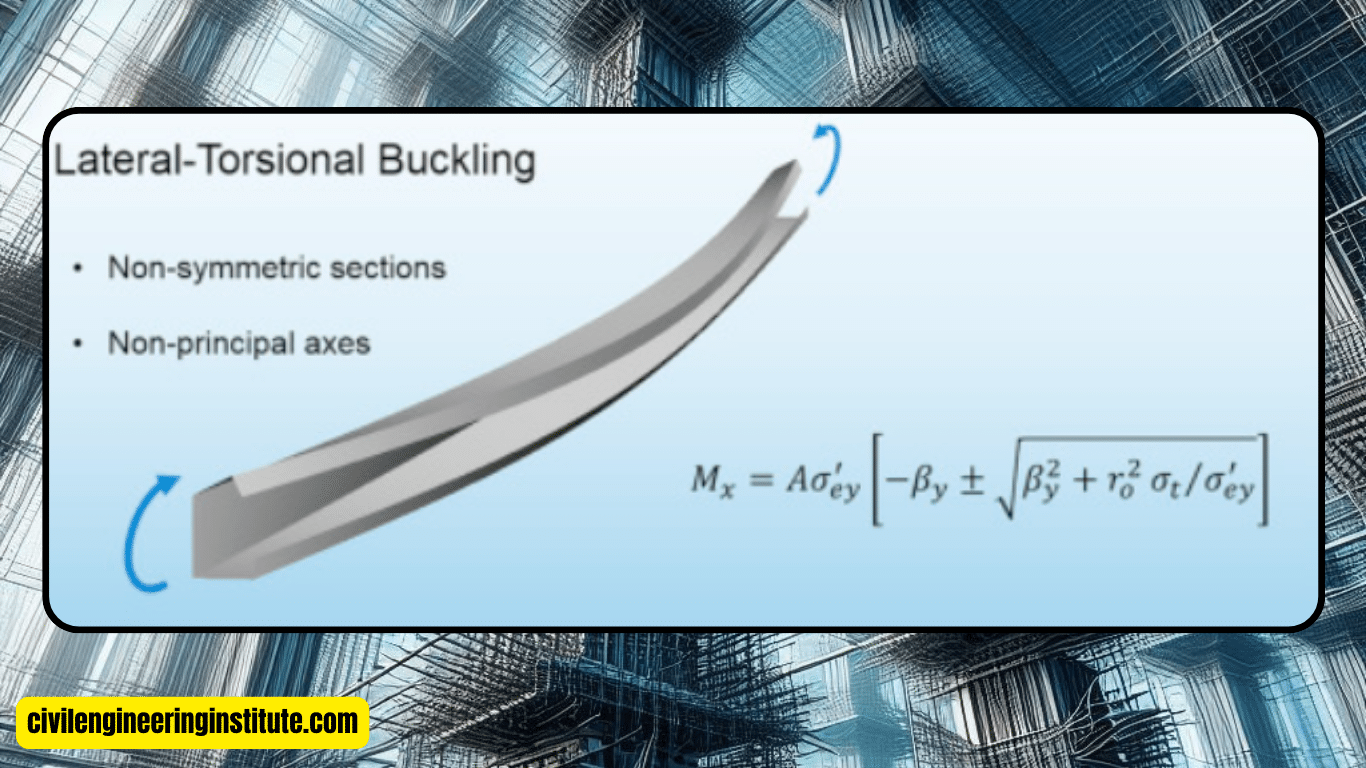
it is important to know how to prevent lateral torsional buckling because it’s crucial to employ some key preventive measures. Firstly, ensure that the structural members, like beams or columns, are adequately designed and sized according to the loads they will bear. This involves consulting engineering standards and codes to determine the appropriate dimensions and material strengths. Additionally, using bracing systems can greatly enhance the stability of the structure, especially in cases where long spans or slender members are involved.
Regular inspections and maintenance are also vital to detect any signs of deformation or stress early on, allowing for timely intervention. By prioritizing proper design, implementation of bracing, and ongoing maintenance, you can effectively mitigate the risk of lateral torsional buckling in your structures.
How to Prevent Lateral Torsional Buckling in Your Structures
Lateral torsional buckling is a critical concern in structural engineering, particularly in long-span beams or columns. It occurs when a load causes the member to bend and twist simultaneously, leading to instability and potential failure. Preventing lateral torsional buckling requires careful consideration of design, materials, and construction methods.
Design Considerations for Prevention
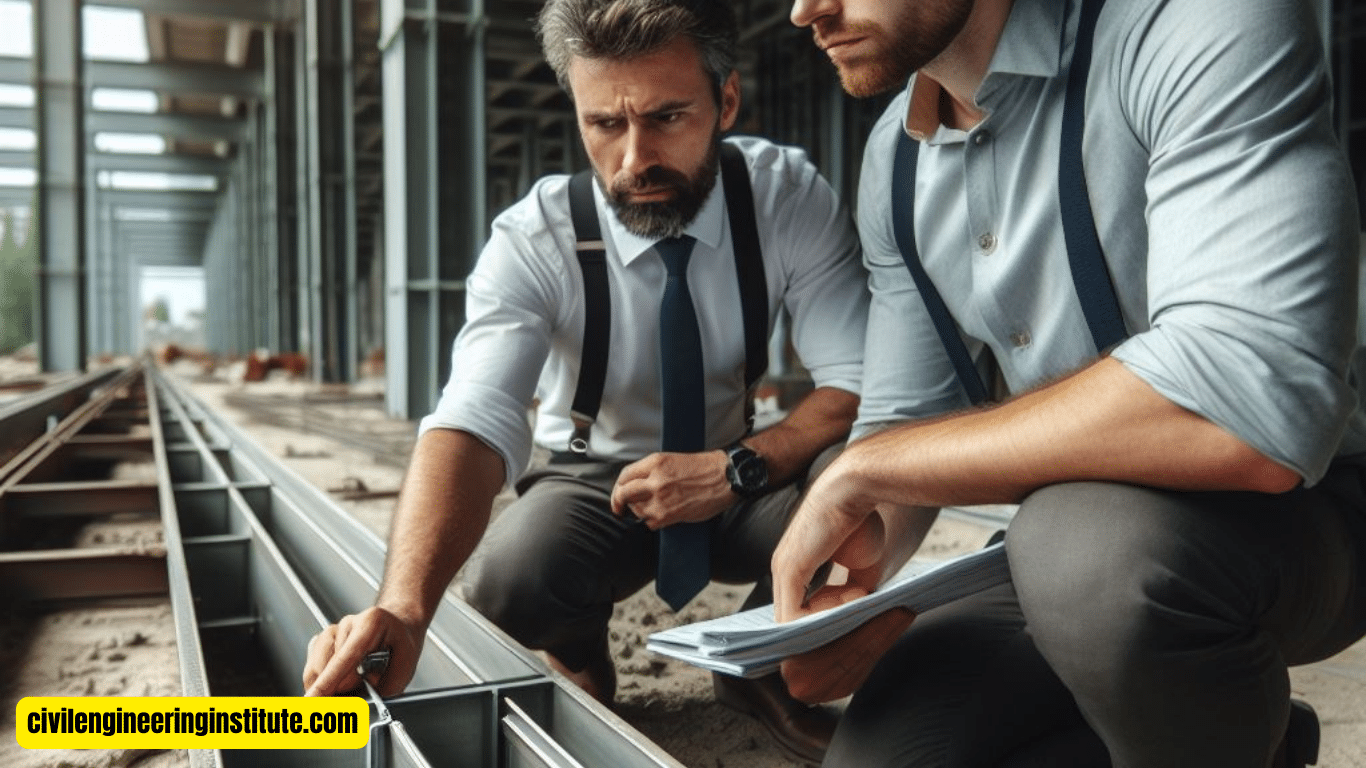
Proper design is paramount in preventing lateral torsional buckling. Engineers must calculate the loads the structure will bear and select appropriate beam sizes and materials accordingly. Factors such as the beam’s length, cross-sectional shape, and support conditions all play a role in determining its susceptibility to buckling.
Choosing the Right Materials
Selecting the right materials can significantly reduce the risk of lateral torsional buckling. High-strength steel or reinforced concrete beams offer greater resistance to bending and twisting forces compared to weaker materials. Additionally, composite materials, such as steel-concrete composite beams, can provide enhanced stability and performance.
Implementing Effective Bracing Systems
Bracing systems are essential for reinforcing structural members and preventing lateral torsional buckling. Diagonal braces, cross-bracing, or shear walls can help distribute loads evenly and resist bending and twisting forces. These systems are particularly crucial in long-span structures where the risk of buckling is higher.
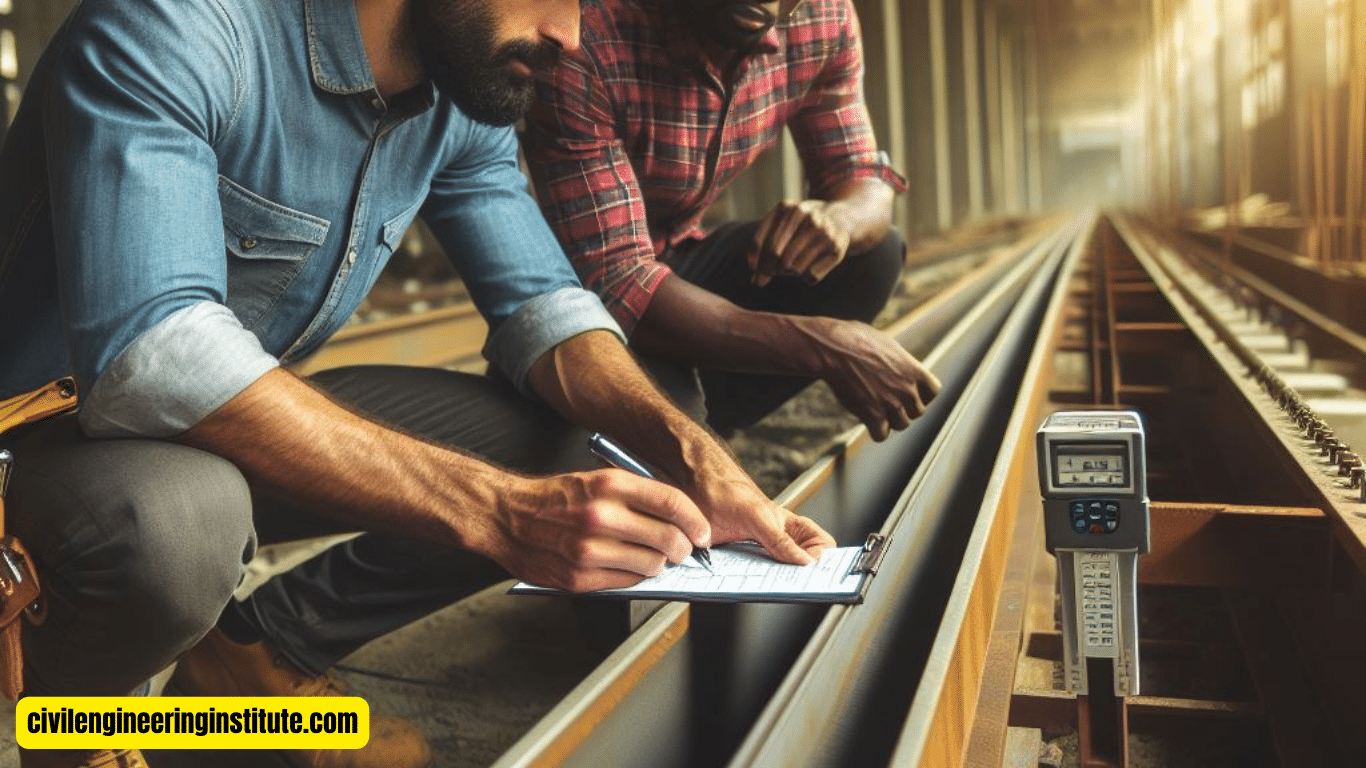
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Regular inspections and maintenance are vital for detecting early signs of lateral torsional buckling. Engineers and building owners should regularly assess the condition of structural members, looking for any signs of deformation, cracking, or stress. Timely intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating into major structural failures.
Some key points: How to prevent lateral torsional buckling
How to Counter Lateral Torsional Buckling
To counter lateral torsional buckling, engineers employ various techniques aimed at enhancing the stability of structural members, particularly beams and columns. These techniques include proper design considerations, material selection, implementation of bracing systems, and regular inspections and maintenance.
Causes of Lateral Torsional Buckling
Lateral torsional buckling occurs when a structural member, such as a beam or column, is subjected to compressive forces along its length, leading to bending and twisting. Long spans, insufficient bracing, inadequate material strength, or poor design are a few factors that frequently make this phenomenon worse.
Preventing Buckling in Beams
Preventing buckling in beams involves ensuring that the beams are adequately sized, designed, and supported to resist bending and twisting forces. Engineers carefully consider factors such as beam length, cross-sectional shape, material properties, and support conditions to mitigate the risk of buckling.
Factors Affecting Lateral Torsional Buckling Strength
Several factors can affect the lateral torsional buckling strength of structural members, including their size, shape, material properties, and loading conditions. Additionally, the presence of bracing systems and the level of support provided can significantly influence the member’s resistance to buckling.
When to Check for Lateral Torsional Buckling
It’s essential to check for signs of lateral torsional buckling during the design, construction, and ongoing maintenance phases of a structure. Regular inspections should be conducted to detect any indications of deformation, cracking, or stress in the structural members, allowing for timely intervention to prevent buckling.
Difference Between Lateral Torsional Buckling and Buckling
While both lateral torsional buckling and buckling involve structural instability, they occur in different ways. Buckling typically refers to the sudden failure of a slender column or member under compressive loads, whereas lateral torsional buckling involves both bending and twisting of a member due to combined compressive and bending forces.
Limit the State of Lateral Torsional Buckling
The limit state of lateral torsional buckling is reached when a structural member experiences sufficient bending and twisting forces to cause instability and potential failure. Engineers must ensure that the design and construction of the structure meet or exceed the required safety standards to prevent reaching this limit.
Lateral Torsional Buckling Slenderness
Lateral torsional buckling slenderness refers to the ratio of a structural member’s length to its depth or width. Members with higher slenderness ratios are more susceptible to buckling, requiring careful consideration of design and reinforcement to prevent instability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preventing lateral torsional buckling requires a proactive approach that begins with careful design and material selection. By implementing effective bracing systems and conducting regular inspections, engineers can minimize the risk of structural instability and ensure the safety and longevity of their buildings and bridges. By following these preventive measures, you can safeguard your structures against the threat of lateral torsional buckling.
FAQs
What is lateral torsional buckling, and why is it a concern?
Lateral torsional buckling happens when a long beam or column bends and twists, which can lead to structural instability and failure.
How does lateral torsional buckling occur?
It occurs when a load causes a structural member to bend and twist simultaneously, typically due to inadequate support or excessive loads.
What factors contribute to lateral torsional buckling?
Factors like beam length, cross-sectional shape, material strength, and support conditions can all influence the risk of buckling.
Can lateral torsional buckling be prevented?
Yes, it can be prevented through proper design, material selection, bracing systems, and regular maintenance.
How can I prevent lateral torsional buckling in my structures?
Ensure proper sizing and design of beams, use high-strength materials, implement effective bracing systems, and conduct regular inspections.
Are there specific design guidelines to prevent lateral torsional buckling?
Yes, engineering standards and codes provide guidelines for calculating loads, selecting materials, and designing structures to resist buckling.
Why is bracing important in preventing lateral torsional buckling?
Bracing helps distribute loads evenly and reinforces structural members, reducing the risk of bending and twisting.
When should I check for signs of lateral torsional buckling?
Regular inspections during construction and throughout the lifespan of the structure are crucial to detecting any signs of deformation or stress early on.
What are the consequences of ignoring lateral and torsional buckling?
Ignoring it can lead to structural failure, pose safety risks, and potentially cause damage to property or infrastructure.
Who should I consult for advice on preventing lateral torsional buckling?
Consulting structural engineers or professionals with expertise in structural stability can provide valuable guidance on prevention measures and structural integrity.