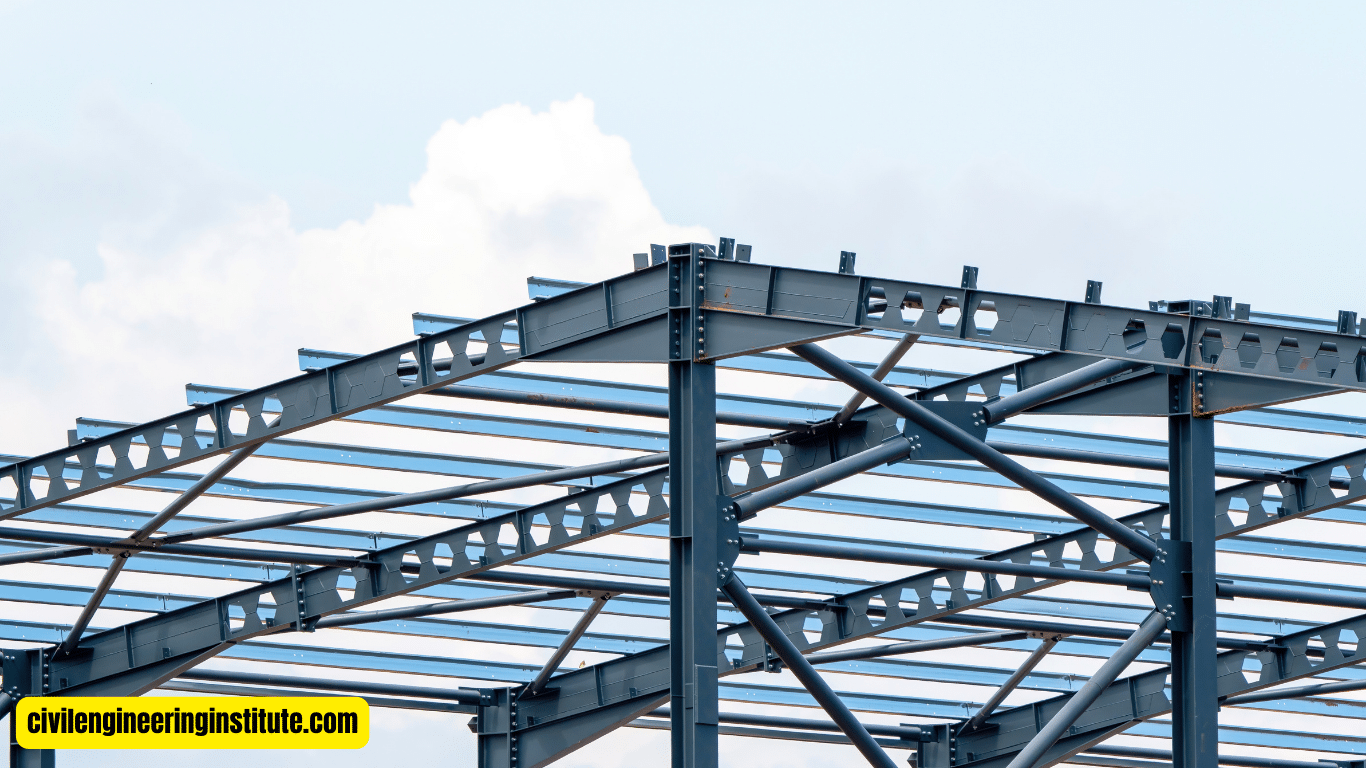
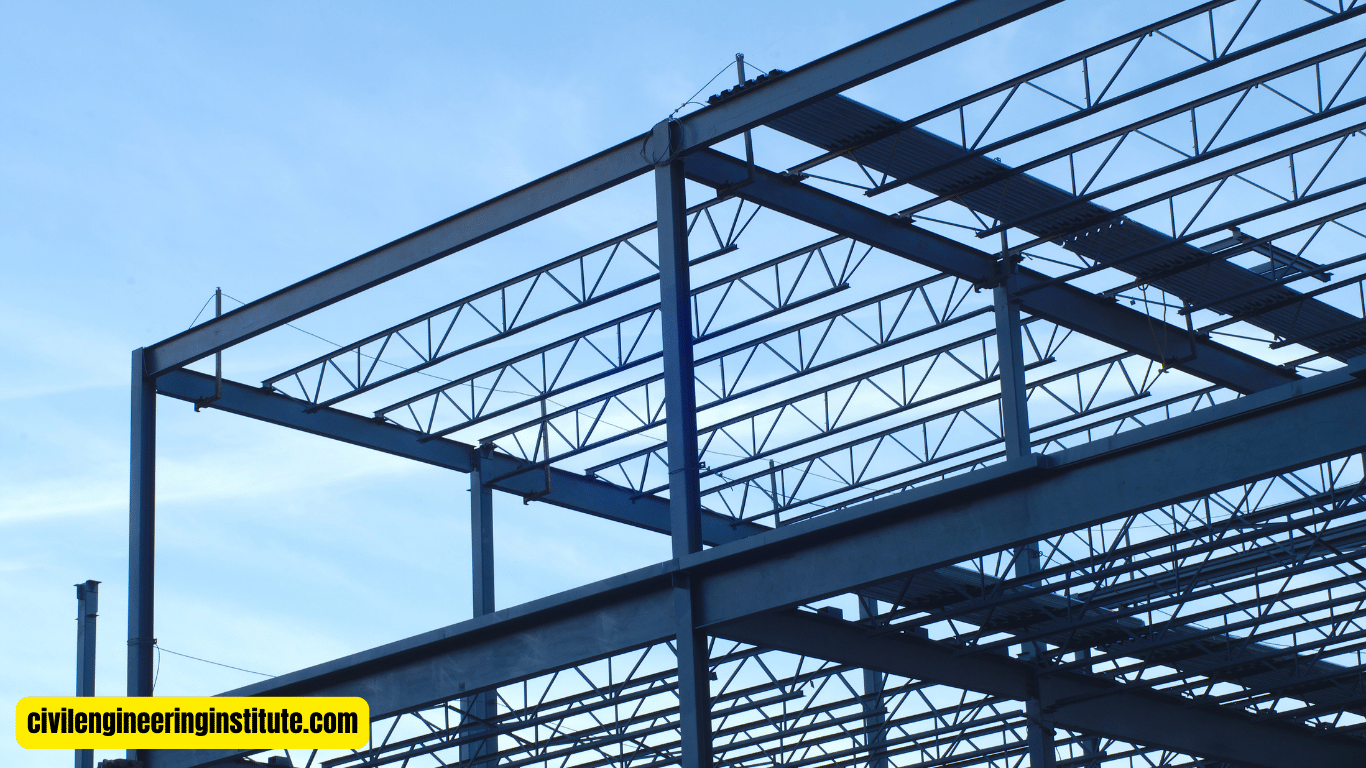
When it comes to constructing sturdy structures, understanding the design of steel beams and columns is crucial. Steel beams and columns provide essential support, ensuring buildings can withstand various loads and pressures over time. The design process involves careful calculations and considerations to ensure the integrity and safety of the structure.
Factors such as the type of steel, beam/column size, and load-bearing capacity are all taken into account during the design phase. Engineers use advanced software and mathematical equations to create precise designs that meet building codes and safety standards. By optimizing the design of steel beams and columns, builders can create durable and resilient structures that stand the test of time.
Design of Steel Beams and Columns: A Comprehensive Guide
Steel beams and columns play a pivotal role in the construction of robust and durable buildings. Understanding the intricacies of their design is essential for engineers and builders alike. In this article, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of designing steel beams and columns, covering everything from material selection to load calculations.
Materials Selection: Choosing the Right Steel
The first step in the design process is selecting the appropriate type of steel for the beams and columns. Different grades of steel offer varying levels of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Engineers must carefully evaluate factors such as the building’s location, environmental conditions, and intended use to determine the most suitable steel grade.
Structural Analysis: Assessing Loads and Forces
Before designing steel beams and columns, engineers conduct a thorough structural analysis to determine the expected loads and forces the structure will encounter. This analysis considers factors such as dead loads (the weight of the structure itself), live loads (occupant loads and furniture), wind loads, and seismic forces. By accurately assessing these loads, engineers can design beams and columns capable of supporting the structure safely.
Beam Design: Sizing and Configuration
Once the loads are determined, engineers proceed to design the steel beams. This involves selecting the appropriate beam size, shape, and configuration to withstand the anticipated loads without deflecting or failing. Common beam shapes include I-beams, H-beams, and channels, each offering unique advantages depending on the application. Engineers use structural analysis software and industry-standard formulas to calculate the required beam dimensions, ensuring structural integrity and safety.
Column Design: Resisting Compression Loads
Columns, like beams, must be designed to support the vertical loads imposed by the structure. However, unlike beams, columns primarily resist compressive forces. Engineers carefully select the column size, shape, and material to prevent buckling and ensure stability under load. Reinforcing elements such as stiffeners and bracing may be incorporated into the column design to enhance strength and rigidity.
Connection Design: Ensuring Structural Stability
In addition to designing individual beams and columns, engineers must pay close attention to how these elements are connected to each other and to other structural members. Proper connection design is crucial for maintaining structural stability and preventing failures due to shear, bending, or torsion. Welded, bolted, and riveted connections are common methods used to join steel beams and columns, with each offering specific advantages depending on the application.
Quality Control: Ensuring Compliance and Safety
Throughout the design process, strict quality control measures are implemented to ensure compliance with building codes and safety standards. Engineers conduct thorough inspections and testing to verify the integrity of the steel beams and columns, including material testing, weld inspections, and dimensional checks. By adhering to rigorous quality control protocols, builders can be confident in the reliability and safety of the structure.
Some important queries: Design of Steel Beams and Columns
How do I design a steel beam step-by-step?
Designing a steel beam involves several steps to ensure it can support the loads it will encounter safely. First, you need to determine the loads acting on the beam, including dead loads (the weight of the structure itself) and live loads (such as people or furniture). Then, calculate the reactions at the supports where the beam will be placed. Next, choose a suitable beam material and shape based on the calculated loads and span length.
Once you have the necessary information, you can use structural engineering principles and software tools to calculate the required beam size and reinforcement, ensuring it meets safety and building code requirements. Finally, perform a thorough analysis and review of the design to ensure its integrity and effectiveness in supporting the structure.
How Do You Design a Steel Column Size?
Designing the size of a steel column involves considering several factors to ensure it can adequately support the vertical loads it will encounter. First, determine the loads the column will bear, including dead loads, live loads, and any additional loads such as wind or seismic forces.
Then, calculate the required column size based on the applied loads and the column’s material properties, including its yield strength and stiffness. Consideration must also be given to the column’s slenderness ratio to prevent buckling. Using structural analysis methods and design codes, engineers can determine the appropriate column size and reinforcement needed to ensure structural stability and safety.
How do I calculate the size of the steel beam required?
To calculate the size of a steel beam required for a specific application, you need to consider several factors, including the loads it will support, the span length, and any other relevant design constraints. First, determine the applied loads on the beam, including dead loads, live loads, and any additional loads such as snow or wind.
Then, calculate the reactions at the beam supports. Using structural analysis methods and engineering principles, select a suitable beam material and shape based on the calculated loads and span length. Finally, use beam design equations or structural analysis software to determine the required beam size and reinforcement necessary to meet safety and building code requirements.
What is the formula for the steel beam?
The formula for calculating the size of a steel beam depends on various factors, including the applied loads, span length, material properties, and design constraints. The bending stress formula, however, is frequently used in beam design and connects the applied loads, beam geometry, and material properties to the maximum stress that the beam will experience.
The bending stress formula is typically expressed as σ = M/SS, where σ is the bending stress, M is the bending moment, and S is the section modulus of the beam. Engineers use this formula, along with other structural analysis methods, to design steel beams that can safely support the loads they will encounter.
How do I calculate the column steel quantity?
Calculating the quantity of steel required for a steel column involves determining the cross-sectional area of the column and the spacing and diameter of the longitudinal reinforcement bars. First, calculate the total applied loads on the column, including dead loads, live loads, and any additional loads such as wind or seismic forces. Then, determine the required column dimensions and reinforcement based on the applied loads and structural analysis.
Using design codes and engineering principles, calculate the required steel quantity by considering factors such as the column’s cross-sectional area, concrete cover, and spacing of reinforcement bars. By performing these calculations accurately, engineers can ensure the structural integrity and safety of the steel column.
How do I calculate beam span?
Calculating the span of a steel beam involves determining the distance between its supports, such as columns or walls. To calculate the beam span, first identify the locations of the beam supports and measure the distance between them. This distance represents the clear span of the beam.
Alternatively, to determine the effective span if the beam has multiple supporting points, measure the distance between the two points with the greatest vertical displacement. It’s essential to consider factors such as beam deflection and support conditions when calculating the beam span to ensure the beam can safely support the applied loads without excessive sagging or deformation.
Conclusion
The design of steel beams and columns is a complex yet essential aspect of structural engineering. By carefully selecting materials, conducting thorough structural analysis, and adhering to industry best practices, engineers can create buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also safe and resilient. Whether designing a small residential structure or a large commercial complex, understanding the principles of steel beam and column design is paramount to ensuring the success of any construction project.
FAQs
What is the design process for steel beams and columns?
The design process involves determining the loads the structure will face, selecting suitable materials, calculating beam and column sizes, and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Why are steel beams and columns important in construction?
Steel beams and columns provide essential support for buildings, ensuring they can withstand various loads and pressures over time.
How do engineers choose the right steel for beams and columns?
Engineers consider factors such as strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance when selecting steel grades for beams and columns, based on the building’s location and intended use.
What factors are considered in beam design?
Beam design takes into account the loads it will bear, its material properties, and its shape and size to ensure it can support the structure safely.
How are column sizes determined in steel construction?
Column sizes are determined by considering the applied loads, material properties, and slenderness ratio to prevent buckling and ensure stability.
What formulas are used to calculate beam sizes?
Formulas such as the bending stress formula and structural analysis methods are used to calculate beam sizes based on applied loads, span length, and material properties.
How is the quantity of steel calculated for columns?
The quantity of steel for columns is calculated by considering factors such as cross-sectional area, reinforcement spacing, and design codes to ensure structural integrity.
What role do connections play in steel beam and column design?
Proper connection design is crucial for maintaining structural stability and preventing failures due to shear, bending, or torsion.
How are steel beams and columns inspected for quality?
Steel beams and columns undergo thorough inspections and testing for material quality, weld integrity, and dimensional accuracy to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Why is understanding steel beam and column design important for construction projects?
Understanding design principles ensures that buildings are not only aesthetically pleasing but also safe and resilient, preventing structural failures and ensuring the longevity of the structure.