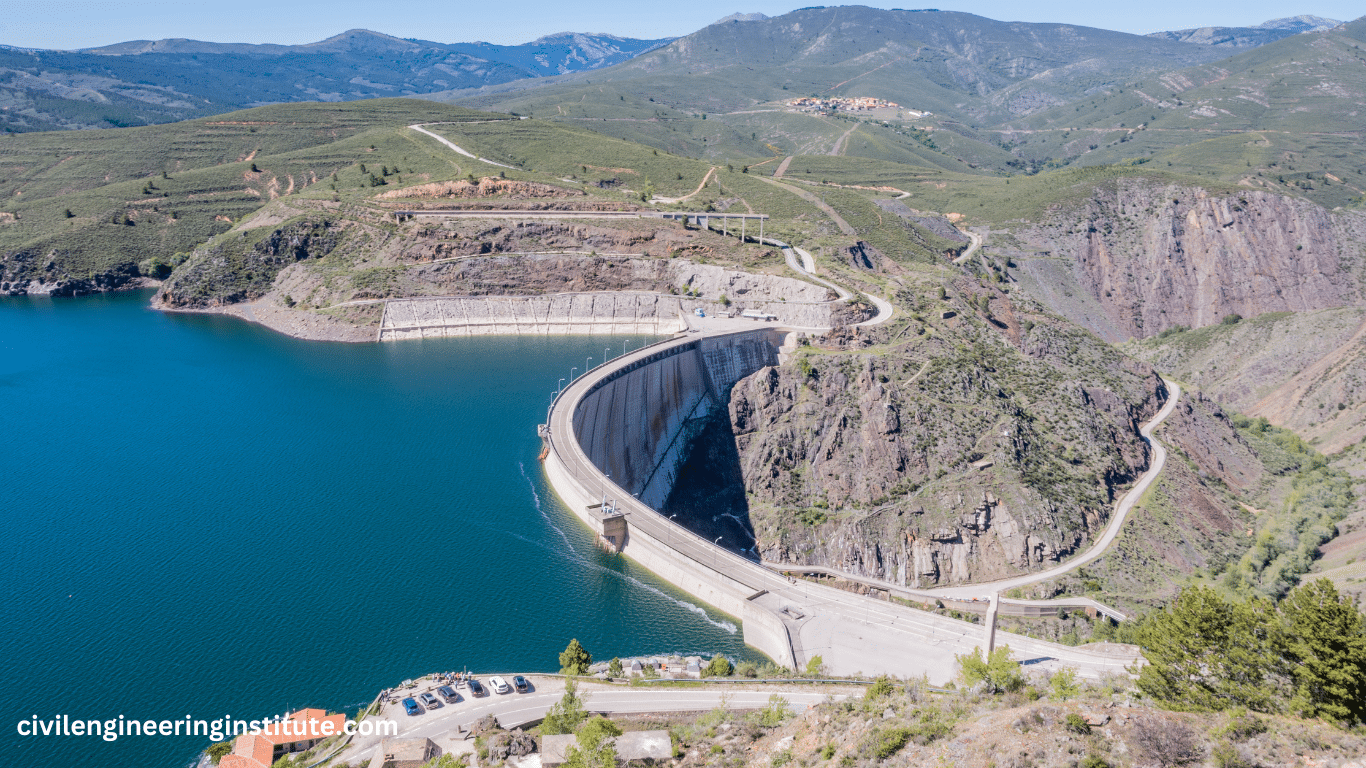
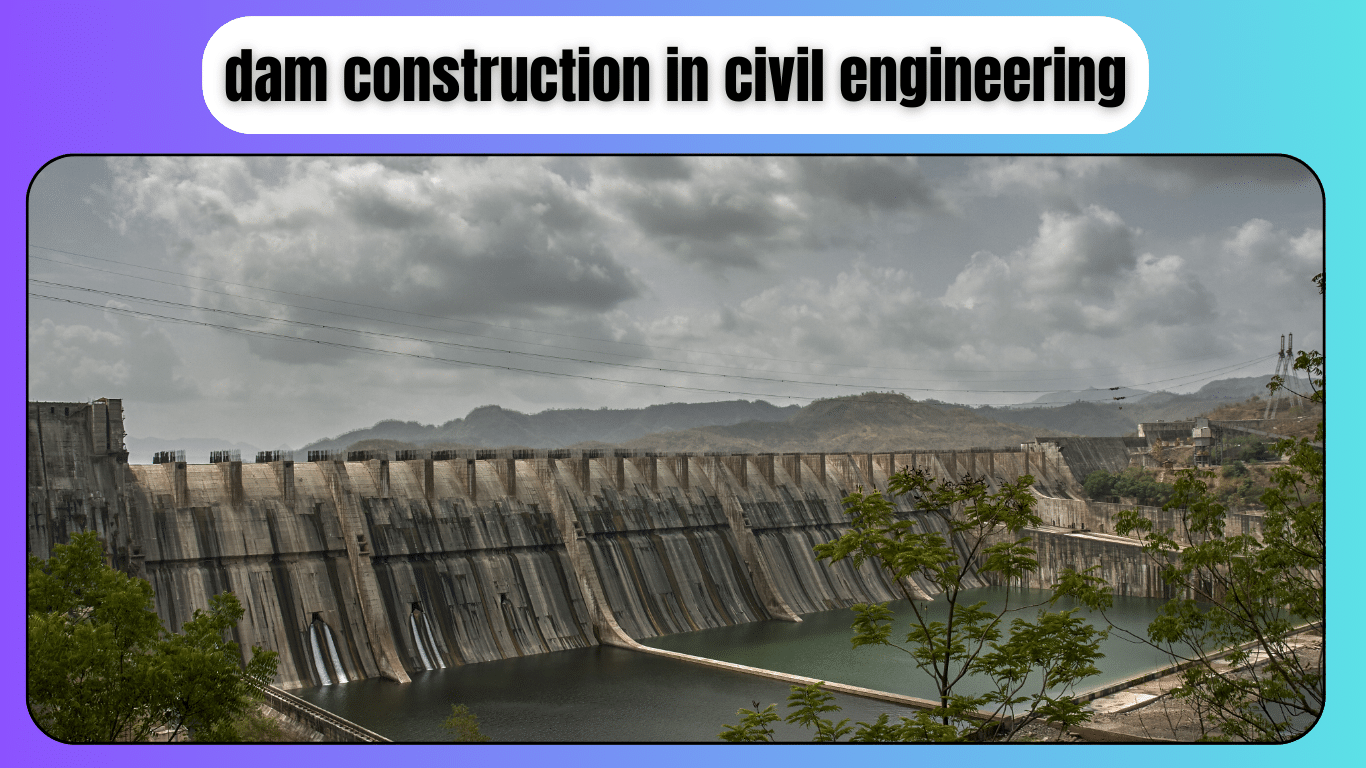
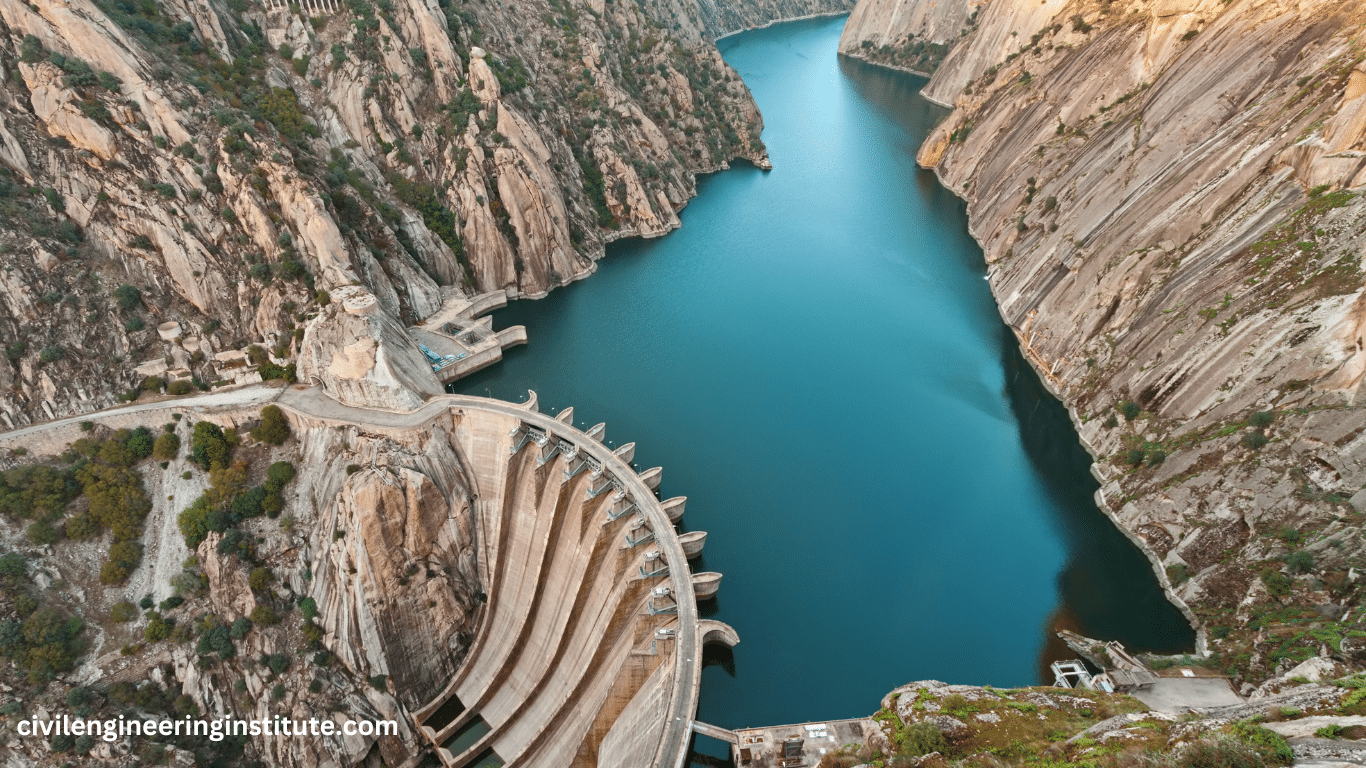
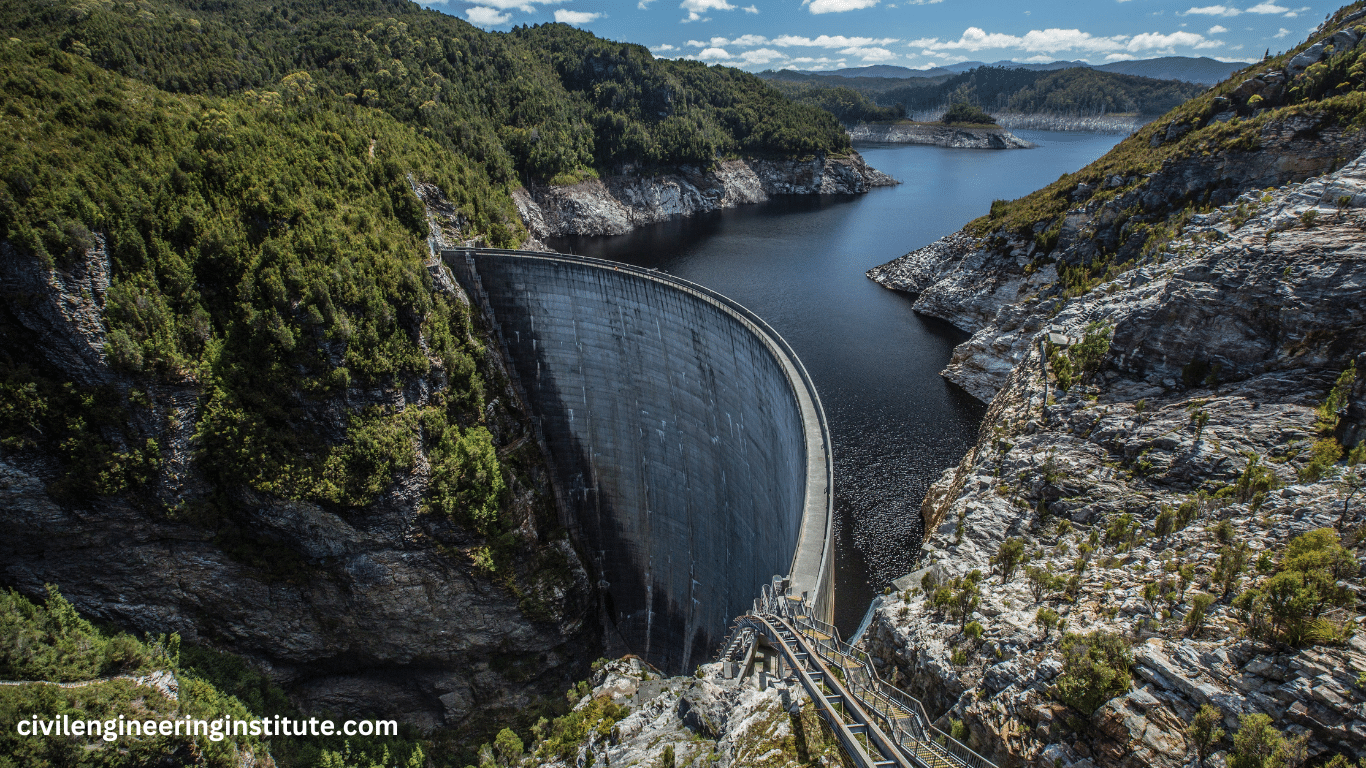
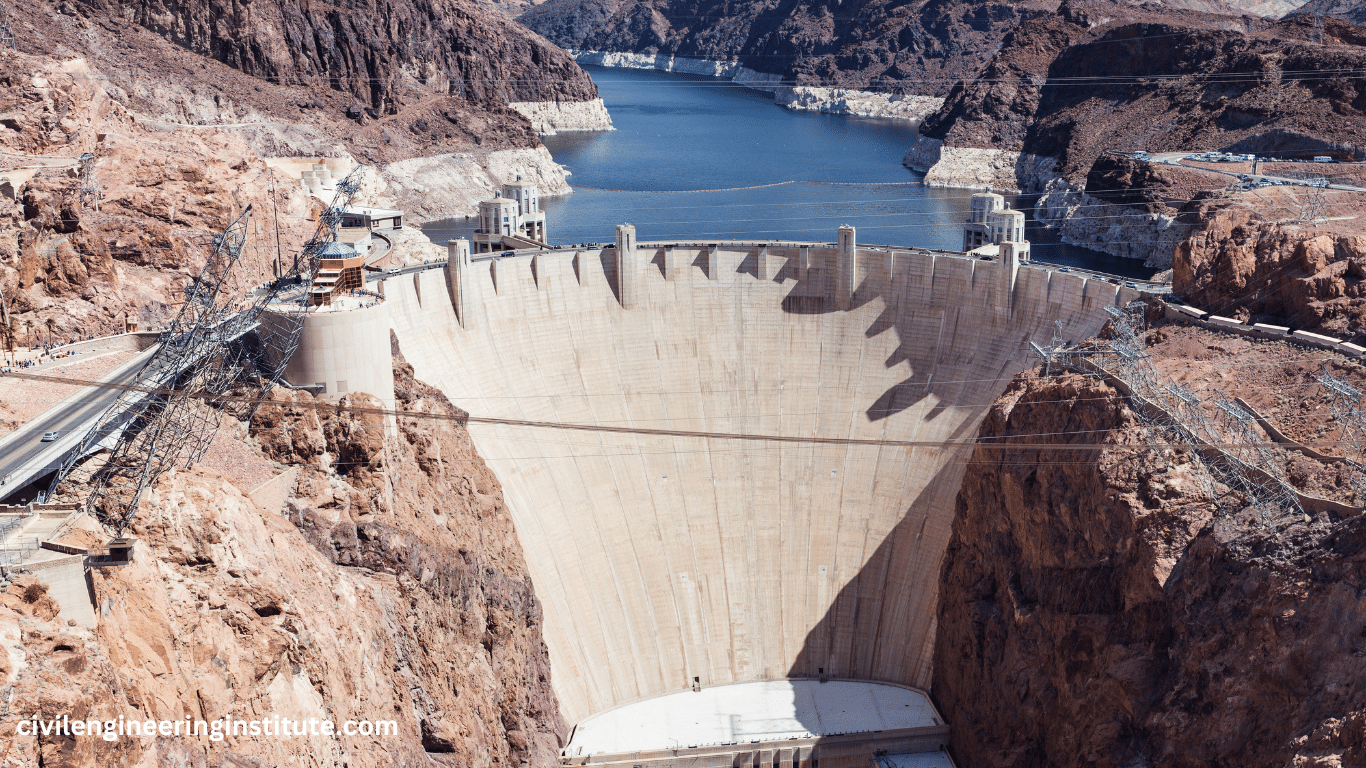
Dam construction in civil engineering is a significant undertaking aimed at managing water resources effectively. Dams are large structures built across rivers or streams to control water flow, store water for various purposes like irrigation, drinking, and electricity generation, and prevent floods. The process involves careful planning, design, and execution to ensure the dam is sturdy and safe. Engineers consider factors such as the type of soil, water flow, and environmental impact during construction.
Concrete and earth are commonly used materials for building dams. Once constructed, dams play a crucial role in providing water for agriculture, industries, and households, while also offering recreational opportunities like boating and fishing. Proper maintenance is essential to ensuring dams remain functional and safe for the surrounding communities.
Dam Construction in Civil Engineering: Harnessing Water for Development
Dam construction stands as one of the most remarkable achievements in civil engineering, shaping landscapes and transforming the relationship between water and human civilization. Dams are monumental structures designed to harness the power of water for various purposes, including irrigation, electricity generation, flood control, and water supply. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of dam construction, exploring its significance, the engineering marvels behind it, and its impact on society and the environment.
What is Dam construction in civil engineering?
Dams, in their simplest form, are barriers built across rivers or streams to impound water, creating reservoirs behind them. These reservoirs serve as storage for water, which can be released as needed for different applications. Dams come in various types, including concrete gravity dams, arch dams, embankment dams, and more, each designed based on factors such as topography, geology, and intended purpose.
Planning and designing dam construction in civil engineering
The process of dam construction begins with meticulous planning and design. Engineers conduct thorough studies of the site to assess factors like hydrology, geology, and environmental impact. They determine the most suitable type of dam for the location and its intended function. Detailed designs are then created, taking into account structural stability, water flow management, and safety measures.
Materials and Construction Techniques
Dams are constructed using a combination of materials and techniques tailored to the specific requirements of each project. Concrete and earth are the primary materials used, with concrete being favored for its strength and durability in large-scale projects. Construction techniques vary depending on the type of dam but typically involve excavation, foundation preparation, placement of materials, and structural reinforcement.
Key Components of Dam Construction
- Foundation Preparation
- Construction of Main Structure
- Spillways and Control Structures
- Environmental Considerations
Foundation Preparation: Before construction begins, the foundation of the dam site must be carefully prepared to ensure stability and prevent seepage. This may involve excavation, grouting, or other soil stabilization techniques to create a solid base for the dam structure.
Construction of the Main Structure: The main structure of the dam is built according to the design specifications. For concrete dams, this often involves pouring concrete into forms and allowing it to cure, creating a solid mass capable of withstanding immense water pressure. On the other hand, to create a stable embankment for an earth dam, materials like compacted earth and other materials are layered.
Spillways and Control Structures: Spillways are essential components of dams designed to safely release excess water during periods of heavy rainfall or flooding. Control structures such as gates and valves are installed to regulate water flow and maintain desired reservoir levels.
Environmental Considerations: During dam construction, environmental considerations are paramount to minimize negative impacts on ecosystems and wildlife habitats. Measures such as fish ladders, sediment traps, and habitat restoration are implemented to mitigate disruptions to natural processes.
Challenges and Innovations
Dam construction poses numerous challenges, ranging from geological obstacles to environmental concerns. Engineers continually innovate to overcome these challenges, developing new materials, construction techniques, and design strategies to enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Environmental Impact
While dams offer significant benefits in terms of water management and energy production, they also have notable environmental impacts. The creation of reservoirs can alter ecosystems, disrupt wildlife habitats, and affect downstream water quality and flow patterns. Mitigating these impacts requires careful planning, monitoring, and mitigation measures.
Key points: Dam construction in civil engineering
Construction of Dams
The construction of dams involves building structures across rivers or streams to control the flow of water. Dams are typically made using materials like concrete or earth, depending on the type of dam and its intended purpose. The process includes extensive planning, site preparation, and the use of specialized equipment and techniques to ensure the dam’s stability and longevity.
Role of Civil Engineers in the Construction of Dams
Civil engineers play a crucial role in the construction of dams. They are responsible for designing the dam structure, ensuring it can withstand the forces of water and other environmental factors. Civil engineers oversee the entire construction process, from site selection and surveying to materials testing and quality control. Their expertise ensures that dams are built safely, efficiently, and in compliance with regulatory standards.
Dams in Civil Engineering
In civil engineering, dams are essential infrastructure designed to store and regulate water for various purposes. Dams serve as reservoirs, providing water for irrigation, drinking, industrial use, and hydroelectric power generation. They also play a vital role in flood control, reducing the risk of downstream flooding during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt.
Methods of Dam Construction
There are several methods of dam construction, including:
- Concrete Gravity Dams
- Embankment Dams
- Arch Dams
- Buttress Dams
Concrete gravity dams are Built using large blocks of concrete stacked on top of each other, relying on their weight to resist the force of water.
Embankment Dams: Constructed by compacting layers of earth or rockfill material to form a barrier against water.
Arch Dams: Curved structures that rely on the arch shape to distribute the force of water to the abutments on either side of the river.
Buttress Dams: Similar to gravity dams but with additional support from buttresses or supports on the downstream side.
Each method has advantages and is chosen based on factors such as the site’s geology, topography, and intended function.
Classification of Dams
Dams can be classified based on various criteria, including:
By Purpose: such as storage dams, diversion dams, or detention dams.
Material: concrete dams, earth dams, rockfill dams, or composite dams.
Structure: gravity dams, arch dams, buttress dams, or embankment dams.
Benefits of Dam Construction
The construction of dams offers numerous benefits, including:
- Providing a reliable source of water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use.
- Generating renewable energy through hydroelectric power generation.
- Controlling flooding by regulating water flow and storing excess runoff.
- Creating recreational opportunities such as boating, fishing, and wildlife habitat preservation.
- Supporting economic development through water supply and energy production.
Types of dams
There are various types of dams, including:
- Concrete Gravity dams are built using mass concrete to resist the force of water.
- Embankment Dams: Made of compacted earth or rockfill material.
- Arch Dams: curved structures that transfer water pressure to the abutments.
- Buttress Dams: supported by buttresses or supports on the downstream side.
Each type has its own advantages and is chosen based on factors such as site conditions and engineering requirements.
Disadvantages of Dams
Despite their benefits, dams also have disadvantages, including:
- Displacement of communities and loss of habitat due to reservoir inundation.
- Altered downstream ecosystems and water flow patterns.
- Sedimentation builds up behind the dam, reducing storage capacity over time.
- Potential for dam failure or breaches, leading to catastrophic flooding.
- Environmental and social impacts, such as the loss of biodiversity and cultural heritage.
Dam Material
Dams can be made from various materials, including concrete, earth, rockfill, and steel. The choice of material depends on factors such as the site’s geology, construction costs, and structural requirements.
Height of a Dam
The height of a dam varies depending on factors such as the volume of water it needs to impound, the topography of the surrounding area, and engineering considerations. Dams can range from small structures a few meters high to towering megaprojects over a hundred meters tall.
Dam Measurement
The measurement of dams involves assessing various parameters such as height, length, width, and storage capacity. Engineers use surveys, topographic maps, and hydrological data to accurately measure and monitor dams to ensure they function as intended and remain safe for surrounding communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dam construction represents a remarkable feat of engineering that has shaped the course of human history by harnessing the power of water for development. From ancient civilizations to modern-day megaprojects, dams have played a vital role in supplying water, generating electricity, and protecting communities from floods. However, their construction and operation must be approached with careful consideration of environmental and societal impacts to ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
FAQs
What are the main types of dams in civil engineering?
This question addresses the various classifications of dams, including concrete gravity dams, arch dams, embankment dams, and more, providing an overview of the different structures used in dam construction.
How do civil engineers assess the site for dam construction?
This FAQ covers topics like geology, hydrology, and environmental impact studies as part of the site assessment process that civil engineers carry out before beginning dam construction.
What are the key challenges in dam construction?
Here, users can find information on the common challenges faced during dam construction, such as geological instability, environmental concerns, and logistical hurdles, offering insights into the complexities of the process.
What is the role of technology in modern dam construction?
This question explores the advancements in technology and their applications in dam construction, including tools for surveying, monitoring, and construction techniques, highlighting innovations shaping the industry.
What environmental considerations are addressed during dam construction?
Users seeking information on the environmental impacts of dam construction can find answers here, including measures taken to mitigate habitat disruption, water quality concerns, and ecosystem preservation.
How are dams designed to withstand natural disasters like earthquakes and floods?
This FAQ addresses the engineering principles behind designing dams to withstand natural disasters, providing insights into seismic retrofitting, flood control mechanisms, and emergency response planning.
What are the economic benefits of dam construction?
Here, users can learn about the economic advantages associated with dam construction, including job creation, energy production, water supply for agriculture, and infrastructure development in remote areas.
What are the steps involved in building a dam from start to finish?
This question provides a step-by-step overview of the dam construction process, covering planning, design, site preparation, construction techniques, and post-construction monitoring and maintenance.
What are the different materials used in dam construction?
Users can find information on the materials commonly used in dam construction, such as concrete, earth, rockfill, and steel, along with their properties, advantages, and limitations.
What are the safety measures implemented during dam construction?
This FAQ addresses safety protocols and measures implemented to ensure the well-being of workers and surrounding communities during dam construction, covering aspects like site security, hazard prevention, and emergency response plans.